21 Ağustos 2023 Pazartesi
What is Smart Drug in Cancer? How Should Smart Drugs Be Used?

She has been working as a medical oncology specialist at Anadolu Medical Center since 2011.
Hacettepe University Medical School, Ankara 1999
Gazi University Internal Medicine Department, Ankara 2004
Başkent University, Medical Oncology Department, Sub-specialty, Ankara 2007
Acıbadem University, Internal Medicine Department, 2011
European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO), 2011
Prof. Yeşim Yıldırım graduated from Hacettepe University Medical School (Medicine in English) in 1999. After completing her specialty training at the Department of Internal Medicine of Gazi University, she started to work as sub-specialty assistant at the Medical Oncology Department of Başkent University. After becoming a medical oncologist in 2007, she completed her compulsory service at Sivas Numune Hospital between 2007 and 2009. Between 2009 and 2011, she worked as medical oncologist at Acıbadem Kozyatağı Hospital and Acıbadem Maslak Hospital.
In 2010, she continued her studies at Acıbadem University as assistant professor of internal medicine. Passing the qualification exam of European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO)
She became associate professor of medical oncology in 2011. Having joined Anadolu Medical Center the same year, Prof. Yıldırım has still been serving as a medical oncologist.
1. Sancak B, Coşkun U, Günel N, Onuk E, Cihan A, Karamercan A, Yıldırım Y, Özkan S. No association between serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I, vascular endothelial growth factor, prolactin and clinicopathological characteristics of breast carcinoma after surgery. Intern Med J. 2004 Jun;34(6):310-5.
2. Coşkun U, Günel N, Onuk E, Yılmaz E, Bayram O, Yamaç D, Cihan A, Uçan B, Yıldırım Y, Çelenkoğlu G, Özkan S. Effect of different neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens on locally advanced breast cancer. Neoplasma. 2003;50 (3):210-6.
3. Coşkun U, Günel N, Yıldırım Y, Memiş L, Boyacıoğlu ZM. Primary mediastinal yolk sac tumor in a 66-year-old woman. Med Princ Pract. 2002 Oct-Dec;11(4):218-20.
4. Coşkun U, Günel N, Yıldırım Y. Long term survival in a patient with malignant pleural mesothelioma after gemcitabine treatment. Case Reports and Clinical Practice Review, 4, 2-3 (2003).
5. Coşkun U, Günel N, Yıldırım Y, Dursun A. Pulmonary resection in a metastatic breast cancer patient with fourteen years survival: A case report. Case Reports and Clinical Practice Review, 5, 12-13 (2004).
6. Coşkun U, Günel N, Yıldırım Y. Gemcitabine induced pulmonary injury. Case Reports and Clinical Practice Review, 5, 178-179 (2004).
7. Yıldırım Y, Akçalı Z, Özyılkan O. Contraversy in folinic acid administration after Fluorouracil. J Clin Oncol: 23,16,3862 (2005).
8. Yıldırım Y, Akçalı Z, Bilezikci B, Özyılkan O. Primary Gastric Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Stomach: A Case Report. Tumori: ;91:440-442 (2005).
9. Yıldırım Y. Özyılkan O, Akçalı Z, Baştürk B. Drug Interaction Between Capecitabine and warfarin: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Clin Pharmaco Ther 44;2:80-82 (2006).
10. Yıldırım Y, Özyılkan O, Emiroğlu R, Demirhan B, Karakayalı H, Haberal M. Early Diagnosis of cancer in renal transplant patients: A single center experience. Asian Pas J Cancer Prev, 7 ,336-339 (2006).
11. Yıldırım Y, Akçay Y, Özyılkan, Celasun B. Prostate Small Cell Carcinoma and Skin Metastases: A Rare Entity. Medical Principles and Practice, 2008;17(3):250-2.
12. Yıldırım Y, Günel N, Coşkun U, Paşaoğlu H, Aslan S, Çetin A. Serum Neopterin levels in Patients with Breast Cancer. Med Oncol. 2008;25(4):403-407.
13. Yıldırım Y, Günel N, Coşkun U, Bukan N, Sancak B, Aslan S., Çetin A. Serum Big ET-1 levels in Female Patients with Breast Cancer. International Imunnopharmacotherapy 2008 ;8(8):1119-23.
14. Karabulut Z, Yıldırım Y, Abacı I, İlgici D, Özyılkan O. Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma of the gallbladder: a case report. Advances in Therapy 2008; 25(5):520-523.
15. Yıldırım Y, Özyılkan O, Bilezikci B, Akçalı Z, Haberal M. Lack of Influence of COX-2 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinomas on Patient Survival . Asian Pas J Cancer Prev 2008;9: 295-298.
16. Çalıkuşu Z, Yıldırım Y, Akçalı Z, Sakallı H, Bal N, Ünal I, Özyılkan O. The effect of Her-2 expression on cisplatin-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2009;28(1): 97.
17. Çalıkuşu Z, Yıldırım Y, Akçalı Z, Sakallı H, Bal N, Özyılkan O. Prognostic significance of the C-erbB-2 expression in Turkish non-small cell lung cancer patients. Çalıkuşu Z, Yıldırım Y, Akçalı Z, Sakallı H, Bal N, Özyılkan O. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2009;10(3):479-82.
18. Yıldırım Y, Özyılkan O, Çalıkuşu Z, Akçalı Z, Akçay Y, Demirhan B. Management of Elderly patients with Advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Turkey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2009;10:699-700.
19. Yıldırım Y, Akçalı Z, Özyılkan O. Signet-ring cell carcinoma of the colon with leptomeningeal involvement. J Clin Neurosci. 2010 Aug;17(8):1051-3. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2009.10.014.
20. Yıldırım Y, Elagoz S, Koyuncu A, Aydın C, Karadayı K. Management of neuroendocrine carcinomas of the breast: A rare entity.Oncol Lett. 2011 Sep 1;2(5):887-890.
21. Aksoy Özcan U, Tezcanlı E, Yıldırım Y, Garipağaoğlu M. The great mimicker: zona zoster at the mastectomy site causing contralateral intramammary lymph node enlargement. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2012;2012:468576. doi: 10.1155/2012/468576.
22. Yıldırım Y. Onat H. Targeted therapies in metastatic thyroid cancer. MOJ 2013;1:13-19.
23. Aksoy Özcan U, Sağlıcan Y, Yıldız ME, Yıldırım Y, Özveri H, Ocak F, Karaslan E. Evaluatoin of testicular tumor calcificatoin with digital orchiography. Eur Radiol DOI:10.1007/s00330-013-2918-7.
National publications
1. Yıldırım Y, Coşkun O, Coşkun U, Kutlu G, Uysal H, Üçler S, İnan LI, Günel N. invasive Thymoma and Myestania Gravis: a case report: Turkish Journal of Neurology. 2003;9(1):113-117.
2. Coşkun U, Yıldırım Y, Günel N. Importance of Biphosphanates In Treatment of Breast Cancer. TheTurkish Journal of Hematology-Oncology. 2003; 13 (2):109-116.
3. Coşkun U, Yıldırım Y, Yamaç D, Çelenkoğlu G, Günel N. Efficacy of carcinoembryonic antigen in the detection of recurrence in colorectal cancer. Türkiye Klinikleri Journal of Gastroenterohepatology 2003;14(1):1-5.
4. Coşkun U, Yıldırım Y, Ceyhan K, Erekul S, Günel N. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Türkiye Klinikleri Journal of Medical Sciences. 2004;24(1): 106-108.
5. Coşkun U, Yıldırım Y, Günel N. Orbital MALT Lymphoma. Medical Journal of Ankara Training and Research Hospital. 2002;34: 67-68.
6. Yıldırım Y, Üner A, Coşkun U, Günel N. Current Management of Malignant Pleural Effusions. Medical Journal of Ankara Training and Research Hospital. In press.
7. Karakoç A, Toruner F, Ayvaz G, Yetkin I, Yıldırım Y, Çakır N, Arslan M. Relationship of Anthropometrical Measurement With Surrenal Hormones and Atherogenic Risk Factors In Obese Patients. Türkiye Klinikleri Journal of Medical Sciences: In press.
8. Yeşim Yıldırım, Özgür Özyılkan. Complementary and alternative treatment in cancer. Progres;5:225-230 (2004).
9. Yıldırım Y, Sarıtas S, Özyılkan O, Demirhan B. Solid pseudopapiller carcinoma of the Pancreas: a case report. Erciyes Medical Journal, 2007;29(6):474-477.
10. Yeşim Yıldırım, Özgür Özyılkan, Hamdi Karakayalı, Mehmet Haberal. Management of hepatacellular carcinoma 2008;4(18):248-53.
11. Yeşim Yıldırım, Özgür Özyılkan. Thromboembolic complications of cancer and management. Acta Oncologica Turcica: 2010.
Book chapters
1. Yıldırım Y, Özyılkan O: Other Problems: Hiccup, Bleeding, Sweating, Prevention and Treatment of Thromboembolic Complications, Chapter 17, pp196-200. In Handbook of Advanced Cancer Care, Catane R, Cherny NI, Kloke M, TannebergerS, Schrijver D, eds. UK, 2006.
2. Y.Yıldırım. H. Onat. Pregnancy and Cancer. Chapter 31, 331-337. Approach to Cancer Patients (Problems in Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up) Editors: H.Onat, N.M.Mandel 2012.
Areas of Interest

Chemotherapy is a special form of drug treatment aimed at stopping or destroying the growth and reproduction of cancer cells that multiply uncontrollably in the human body and damage healthy tissues.
Each organ that makes up the hormone system plays vital roles for our body.
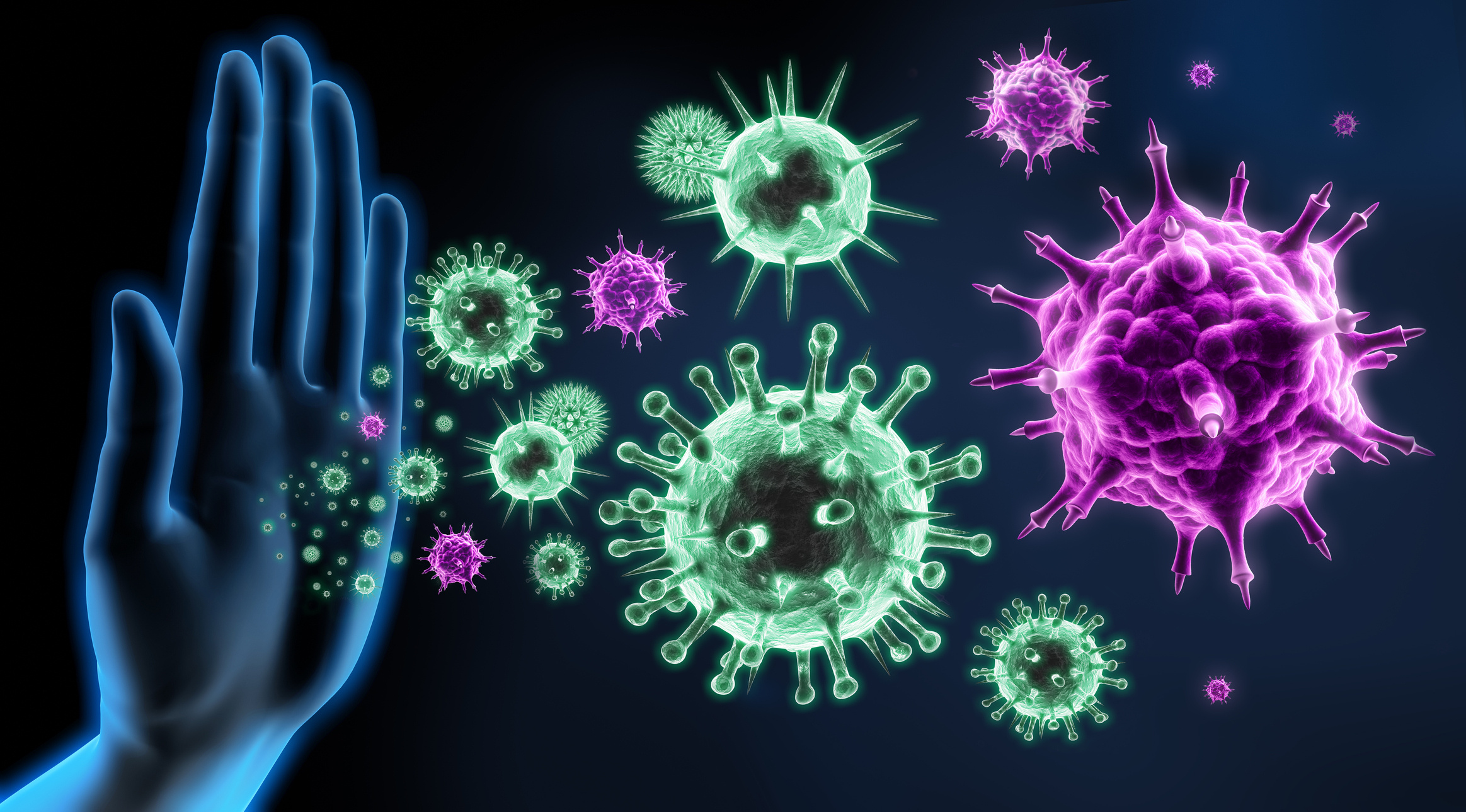
There are ongoing developments in cancer treatment every day. In addition to chemotherapy and radiotherapy methods that have been used for many years, immunotherapy, a type of treatment using drugs, has begun to provide longer-lasting control over cancer in recent years. By activating a person's immune system, immunotherapy enables the individual's own immune cells to fight cancer cells more effectively.

There are ongoing developments in cancer treatment every day. In addition to chemotherapy and radiotherapy methods that have been used for many years, immunotherapy, a type of treatment using drugs, has begun to provide longer-lasting control over cancer in recent years. By activating a person's immune system, immunotherapy enables the individual's own immune cells to fight cancer cells more effectively.
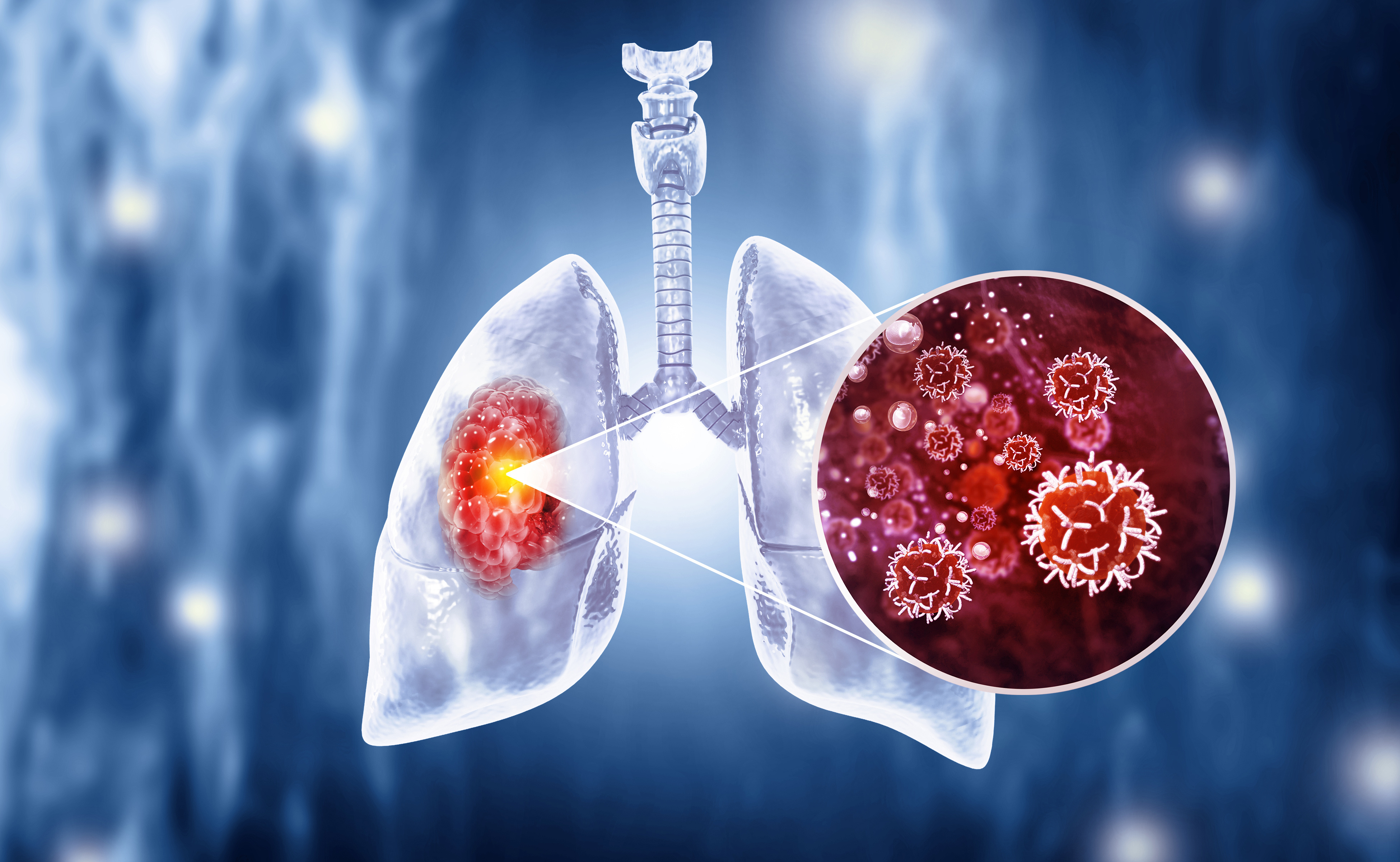
Lung cancer, which ranks first among cancer diseases that lead to death worldwide, is a significant public health issue that causes the death of over 1.7 million people each year. The symptoms and signs that appear in the early stages of the disease are often unnoticed, and critical symptoms like coughing, especially in smokers, are largely overlooked. This situation leads to lung cancer being detected at very late stages, significantly reducing the chances of treatment. Having accurate information about lung cancer, being able to recognize early symptoms, and regularly participating in screening programs in the presence of risk factors are crucial for properly diagnosing and treating lung cancer.
The gallbladder is an organ that is part of the digestive system and plays a role in producing bile, which is necessary for fat metabolism. The gallbladder, which stores and secretes bile, is located in the upper right part of the abdomen. Due to various reasons, changes can begin to occur in the cells of the gallbladder, and these cellular changes may lead to the development of cancer. Gallbladder cancer, which can present with symptoms such as abdominal pain and bloating, is a serious medical condition that requires intervention.
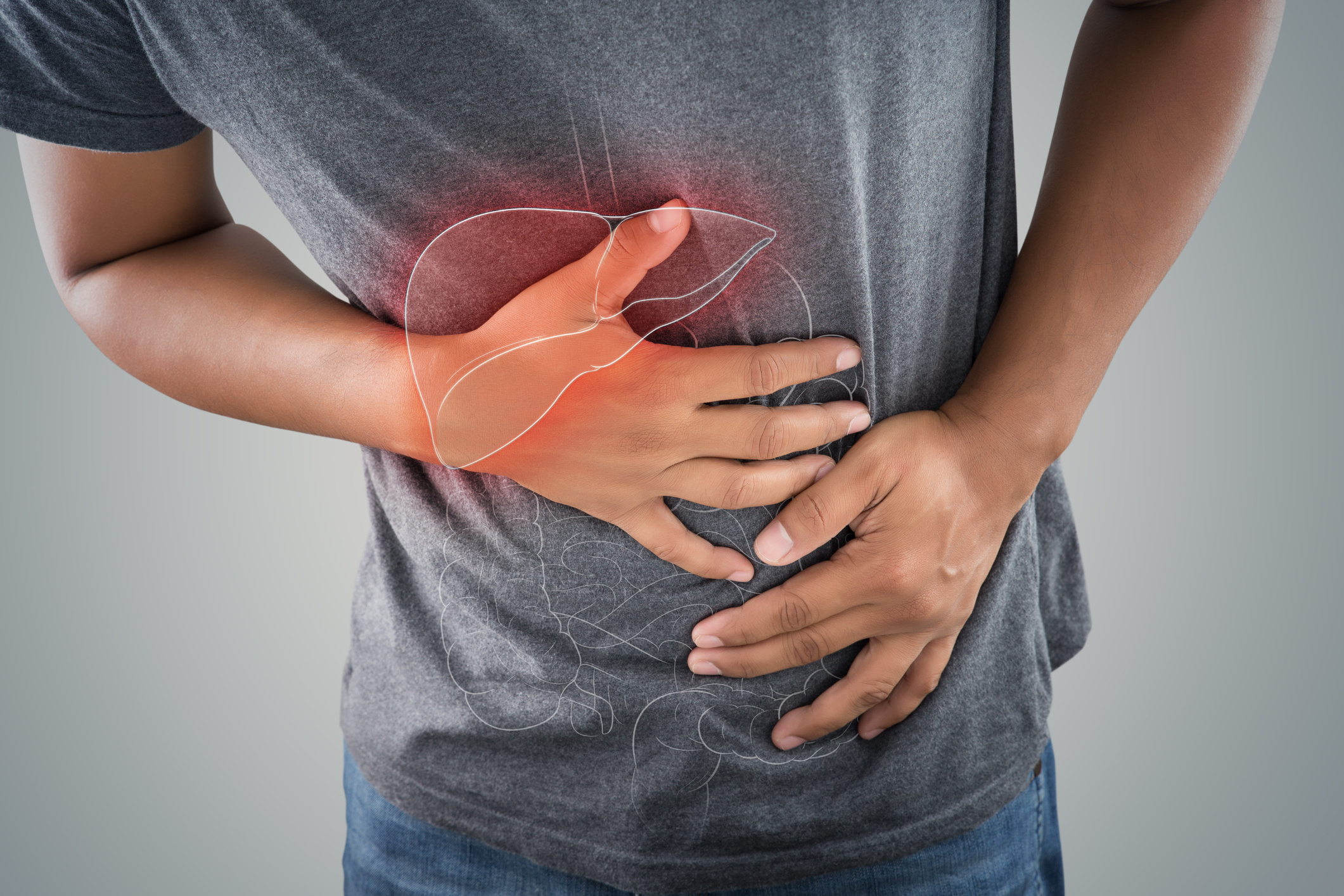
Malignant tumor formations developing within the liver are referred to as liver cancer. The liver is the largest internal organ of the body. It is responsible for performing many vital functions, including the removal of various wastes from the body, absorption of various nutrients, and wound healing. Located in the upper right part of the abdominal region, the liver is also responsible for bile production.

All tissues and organs in the body are made up of different types of cells. Over time, new cells formed by the division of healthy cells replace the cells that die. This process of cell renewal continues throughout a person's life. The timing of when cells should multiply is controlled by DNA. Due to DNA damage, cells may begin to divide unnecessarily. Cancer, one of today's serious diseases, is a condition that arises from the uncontrolled multiplication of the body's own cells.
A tumor is a mass or swelling that arises from the uncontrolled division of body cells, resulting in growth within the affected tissue and/or organ. The cause of most bone tumors is unknown. As the tumor grows, it gradually spreads to healthy tissues, causing them to be replaced by abnormal tissues and weakening the bone, which can lead to pathological fractures. If necessary precautions are not taken, aggressive tumors can cause functional deficiencies within the organ system they develop in and may even threaten life by affecting the entire body's metabolism.
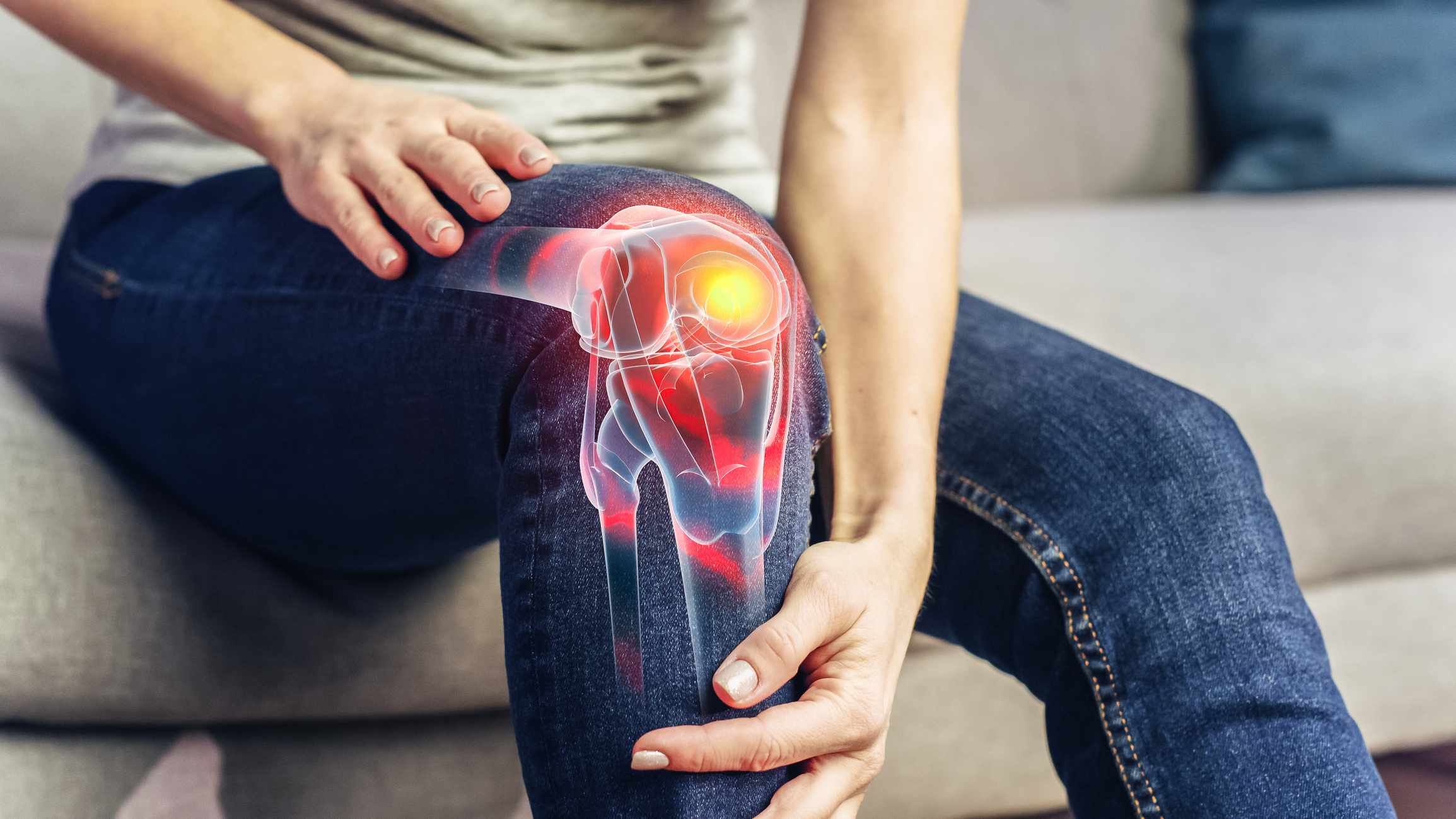

Cancer pain can arise from various causes such as the destruction of normal tissues due to cancer, circulatory disorders caused by blockages in blood vessels, bone fractures related to metastases, infections, inflammation, pressure from the tumor on nerves, or blockages in hollow organs or various channels. It can also result from pain that occurs in the body due to cancer treatment methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
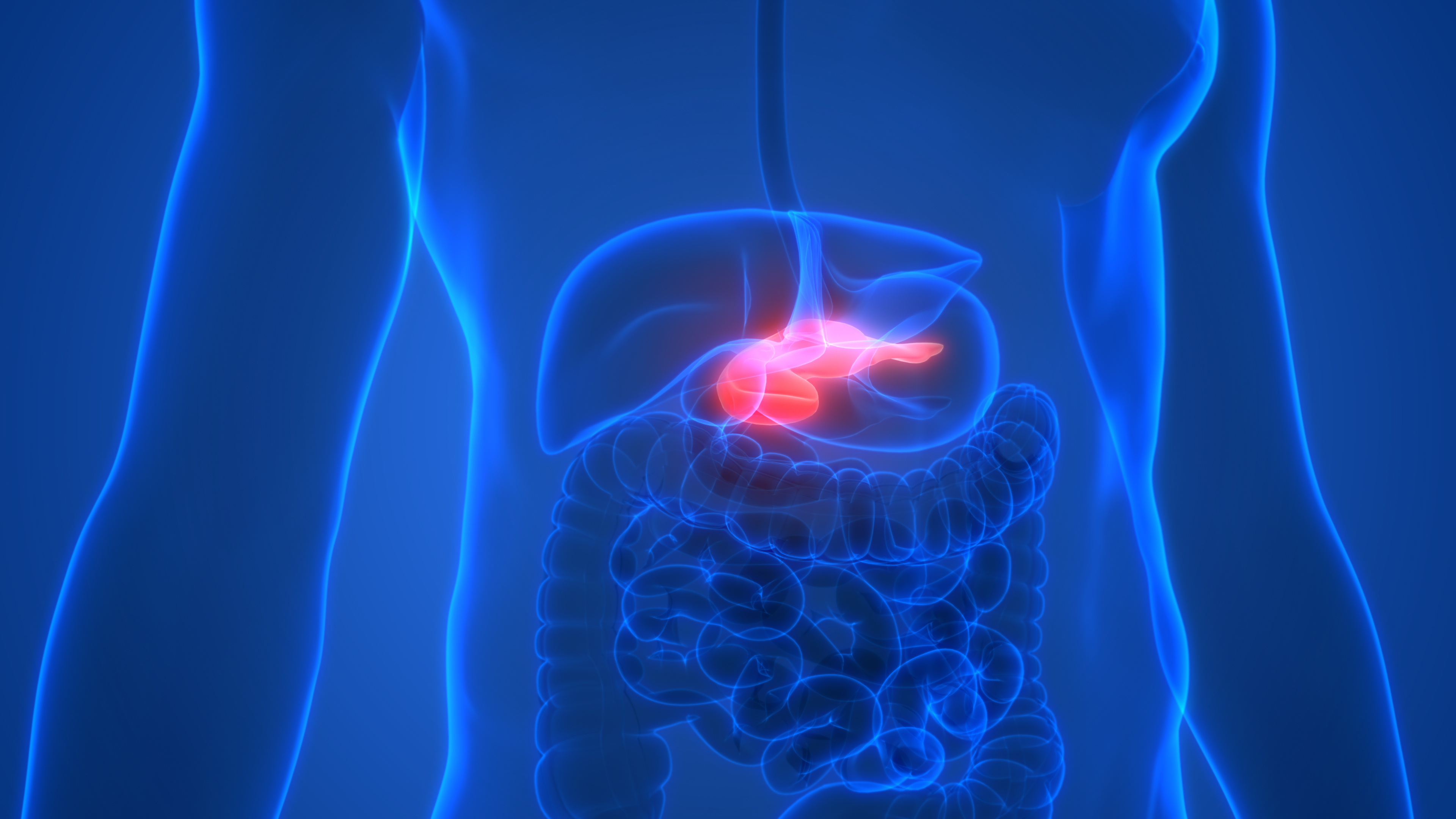
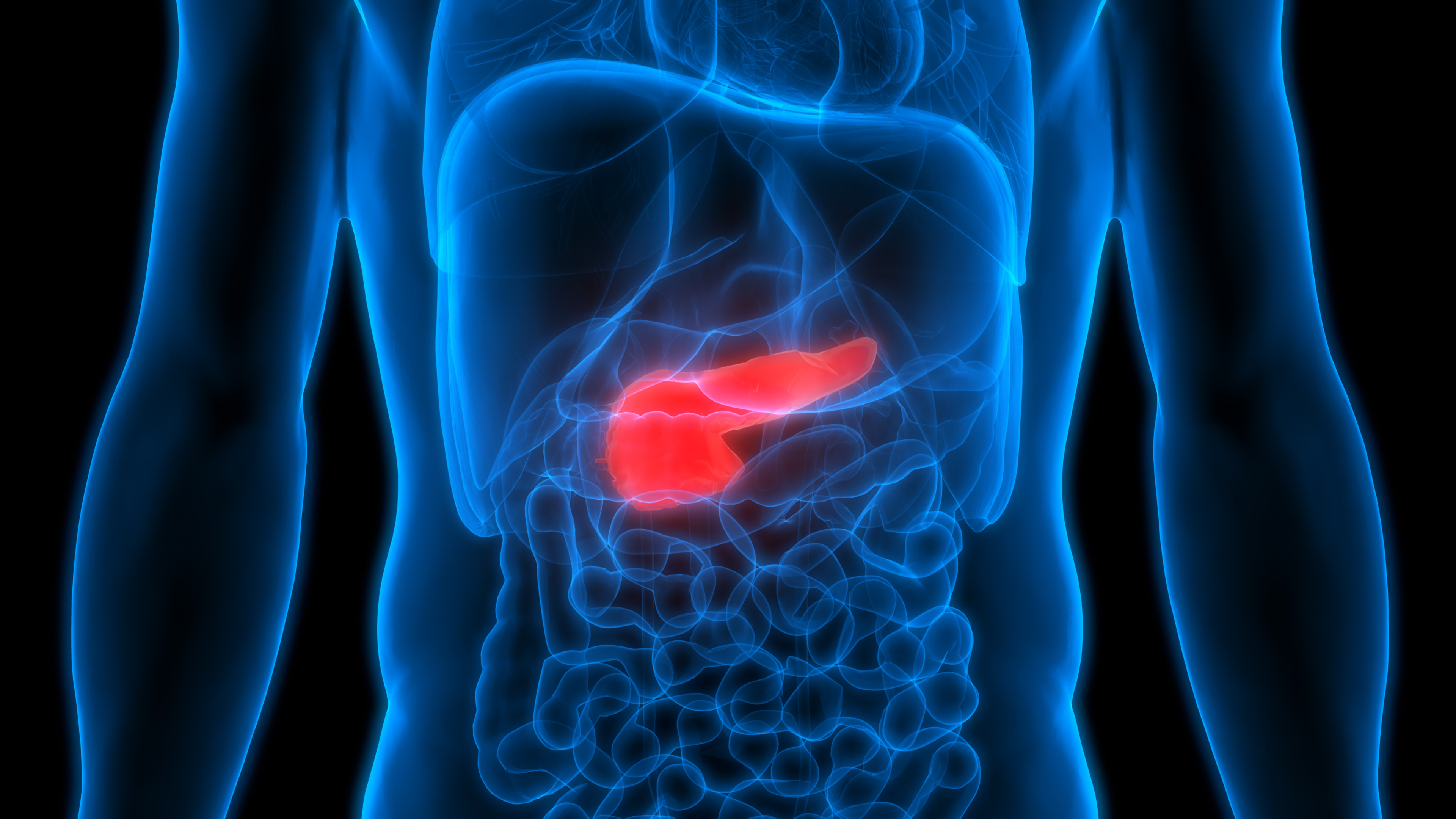
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. What is pancreatic cancer, what are its symptoms, and what is done in treatment? How is the "Whipple technique," one of the most difficult surgeries in the field of general surgery, applied?
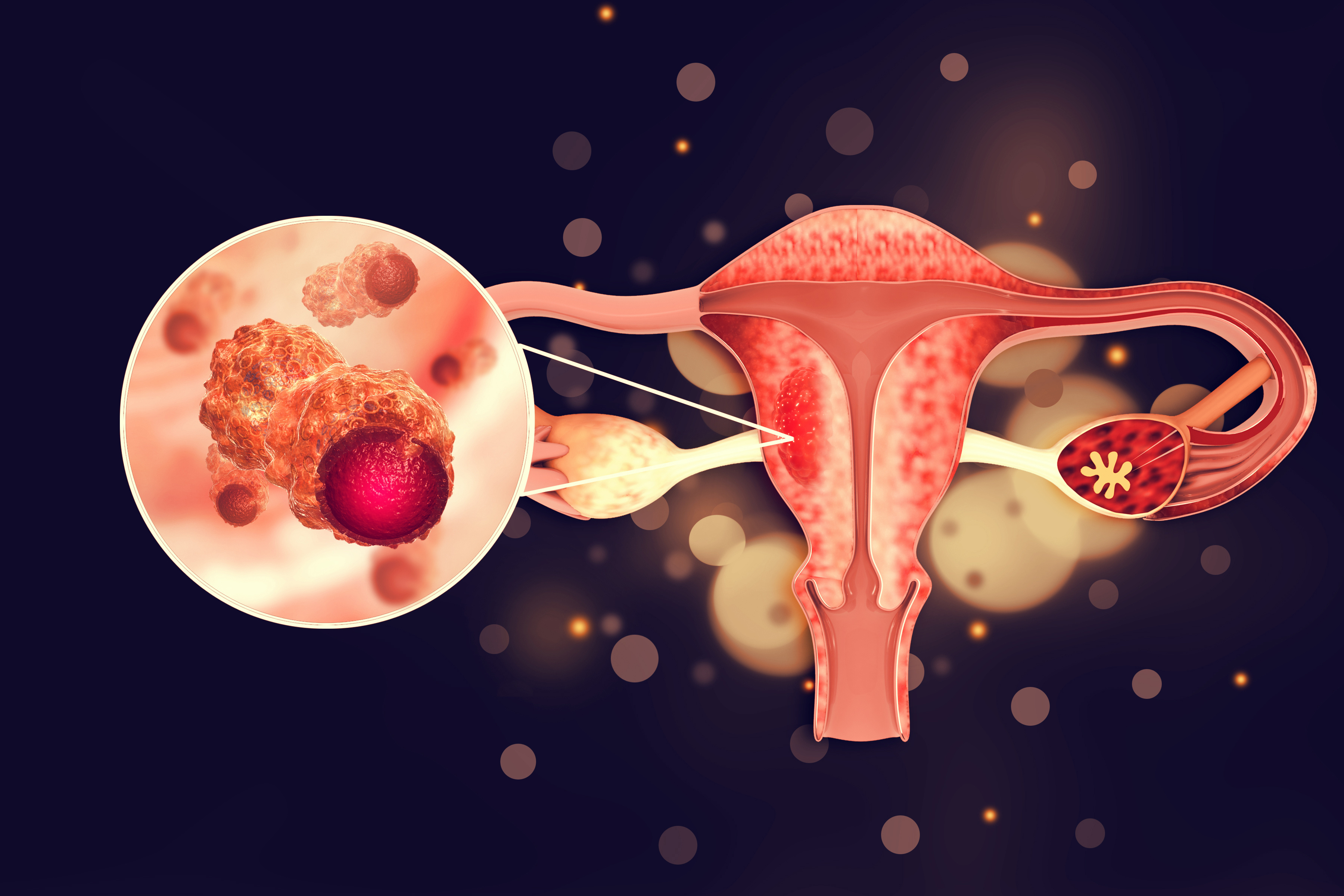
Ovarian cancer is a type of tumor that occurs due to the uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cells in the ovarian or fallopian tube tissue. Ovarian cancer, also known as ovary cancer, is among the most common cancers faced by women worldwide. Diagnosing it can sometimes be difficult because symptoms often develop in the later stages. This can prevent early detection. Commonly experienced symptoms of ovarian cancer can include pelvic pain, abdominal pain, bloating, abnormal bleeding, or vaginal discharge. The goal of ovarian cancer treatment is to remove the tumor from the body. Treatment methods include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiotherapy.

There are ongoing developments in cancer treatment every day. In addition to chemotherapy and radiotherapy methods that have been used for many years, immunotherapy, a type of treatment using drugs, has begun to provide longer-lasting control over cancer in recent years. By activating a person's immune system, immunotherapy enables the individual's own immune cells to fight cancer cells more effectively.
Cancer is a disease that results from the uncontrolled multiplication and growth of cells in any organ or tissue of the body. It is named according to the tissue in which it occurs. More than 200 types have been identified. The most common and fatal types of cancer are lung, stomach, liver, colon, and breast cancer. If cancer spreads from its original site to other organs and tissues, this is called metastasis.
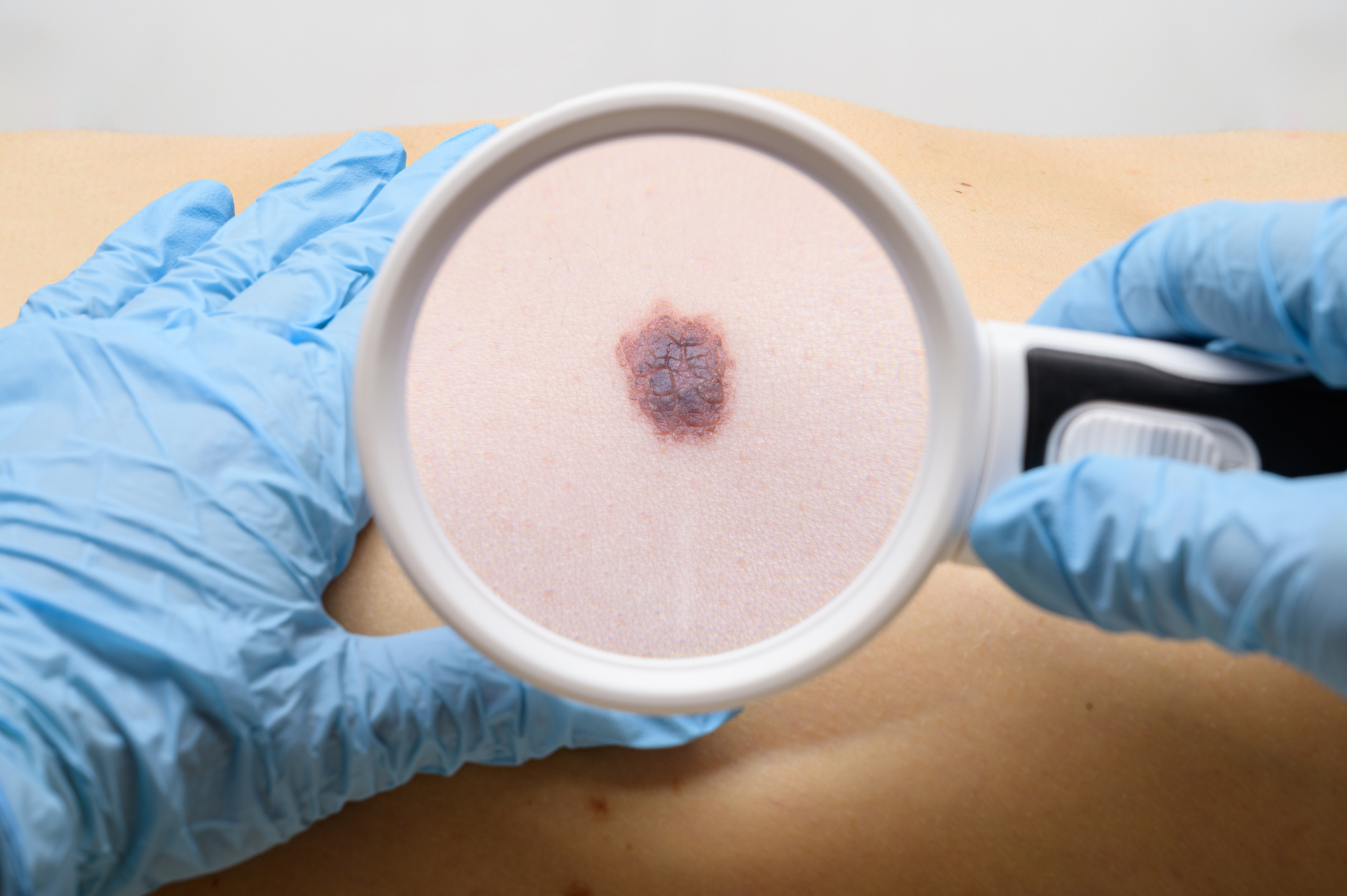
Skin cancer occurs when DNA damage arises in the cells of the skin and this damage is not repaired, leading to uncontrolled proliferation of the damaged cells. More than 99% of skin cancers are composed of three types of cancer.
Laryngeal cancer, also known as throat cancer, is a significant health issue that affects the respiratory tract. The larynx is an organ that plays a crucial role in breathing and sound production. This type of cancer can lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of cells within the larynx, which can spread and result in severe health problems if left untreated.
Cancer is one of the significant health problems threatening human health today, and extensive efforts are being made to find a solution. Despite various diagnostic and treatment methods used so far, an effective method for curing cancer has not yet been established. For this reason, numerous research studies on cancer are being conducted internationally, utilizing various technologies for diagnosis and treatment. One of these methods is liquid biopsy.
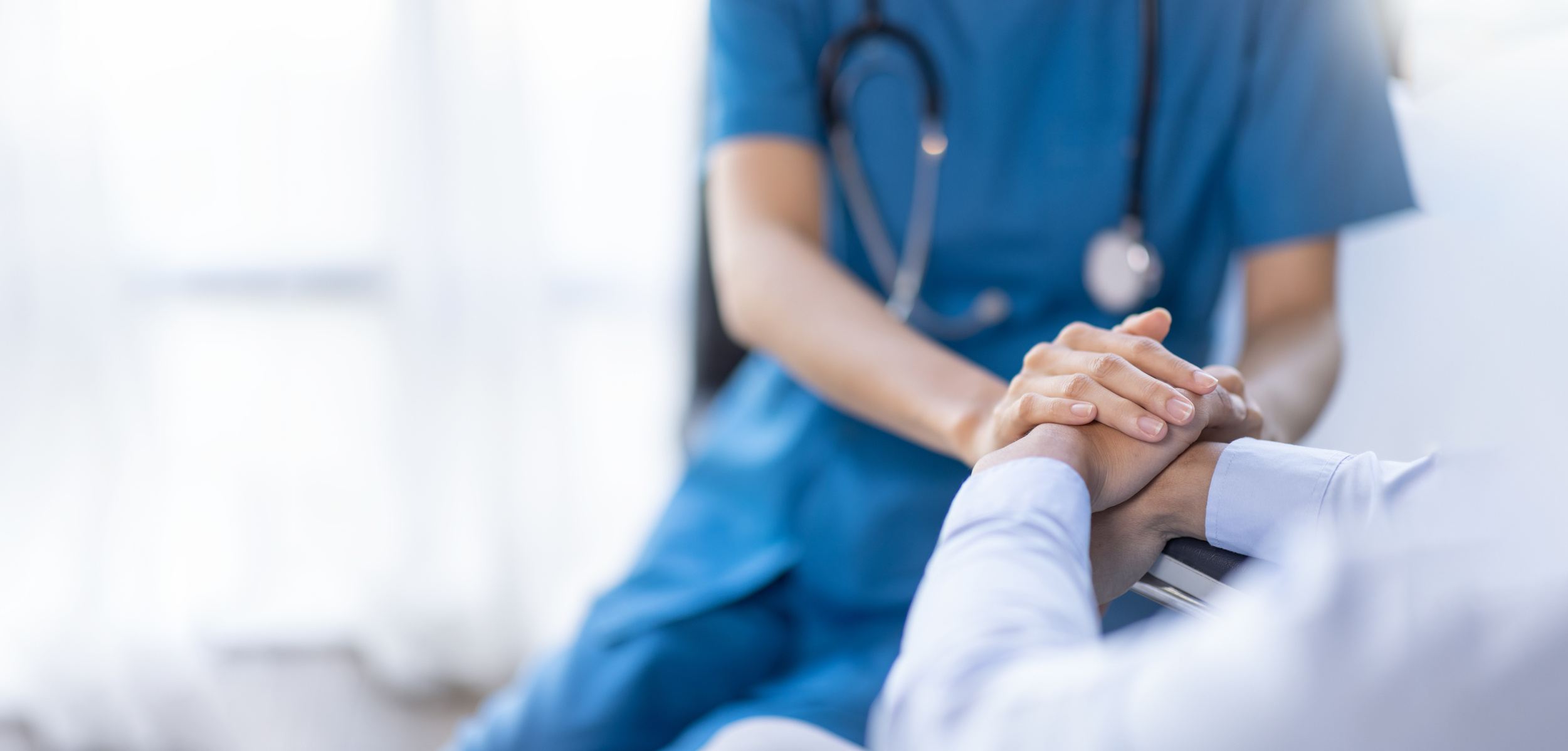

Palliative care is highly effective in reducing the negative impacts experienced by patients and their families during the lifelong treatment process and in alleviating complications related to the disease, thereby improving the quality of life.

Lung cancer, which ranks first among cancer diseases that lead to death worldwide, is a significant public health issue that causes the death of over 1.7 million people each year. The symptoms and signs that appear in the early stages of the disease are often unnoticed, and critical symptoms like coughing, especially in smokers, are largely overlooked. This situation leads to lung cancer being detected at very late stages, significantly reducing the chances of treatment. Having accurate information about lung cancer, being able to recognize early symptoms, and regularly participating in screening programs in the presence of risk factors are crucial for properly diagnosing and treating lung cancer.
Leukemia, commonly referred to as blood cancer, is one of the most prevalent types of cancer. It originates from the bone marrow and the lymphatic system. While some types are primarily seen in children, there are also various types that occur in adults. Early diagnosis is crucial in leukemia, just as it is for all types of cancer. Although leukemia involves a complex treatment process, advancements in methods and strategies are progressively improving outcomes.
The lymphatic system, also known as the lymph or lymphoid system, is associated with both the circulatory and immune systems. This system, which consists of lymph nodes and a network of lymph vessels, circulates a fluid called lymph, made up of blood plasma and white blood cells. These white blood cells play a role in immunity by fighting disease-causing agents. Lymph nodes act as filters, cleaning out foreign disease agents and providing protection against infections and other diseases. Lymphoma, or lymph cancer, occurs due to the uncontrolled growth and proliferation of lymphocytes, the primary cells of the lymphatic system. This disease, which shows varying symptoms depending on the area of involvement, is most commonly found in the lymph nodes.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in women. Every year in our country, thousands of women are diagnosed with cervical cancer, and thousands of women lose their lives due to cervical cancer. It is possible to prevent deaths due to cervical cancer with vaccination and screening.
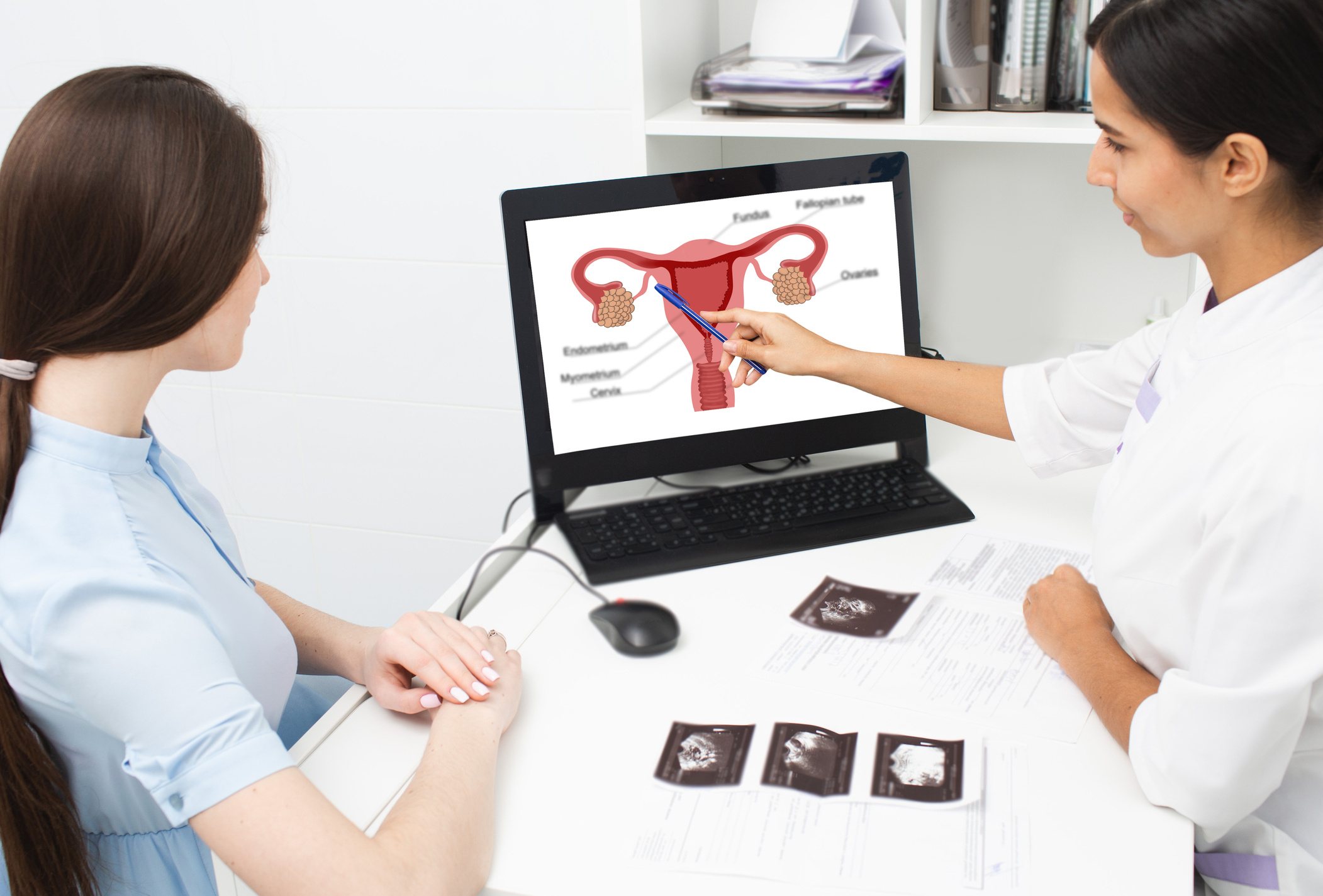
Vulvar cancer refers to malignant tumor formations that can arise on the external surface of the female genital organs. The vulva includes the clitoris and the vaginal lips, known as labia, as well as the skin surrounding the urethra (urinary canal) and vagina. Vulvar cancer often presents as a mass or ulcer that causes itching in the vulva. It can occur at any age but is most frequently diagnosed in older adults. The treatment for vulvar cancer typically involves surgery to remove the cancerous tissue along with a small amount of surrounding healthy tissue. Sometimes, this surgery may require the complete removal of the vulva. The earlier the diagnosis, the less likely it is that extensive surgery will be needed. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
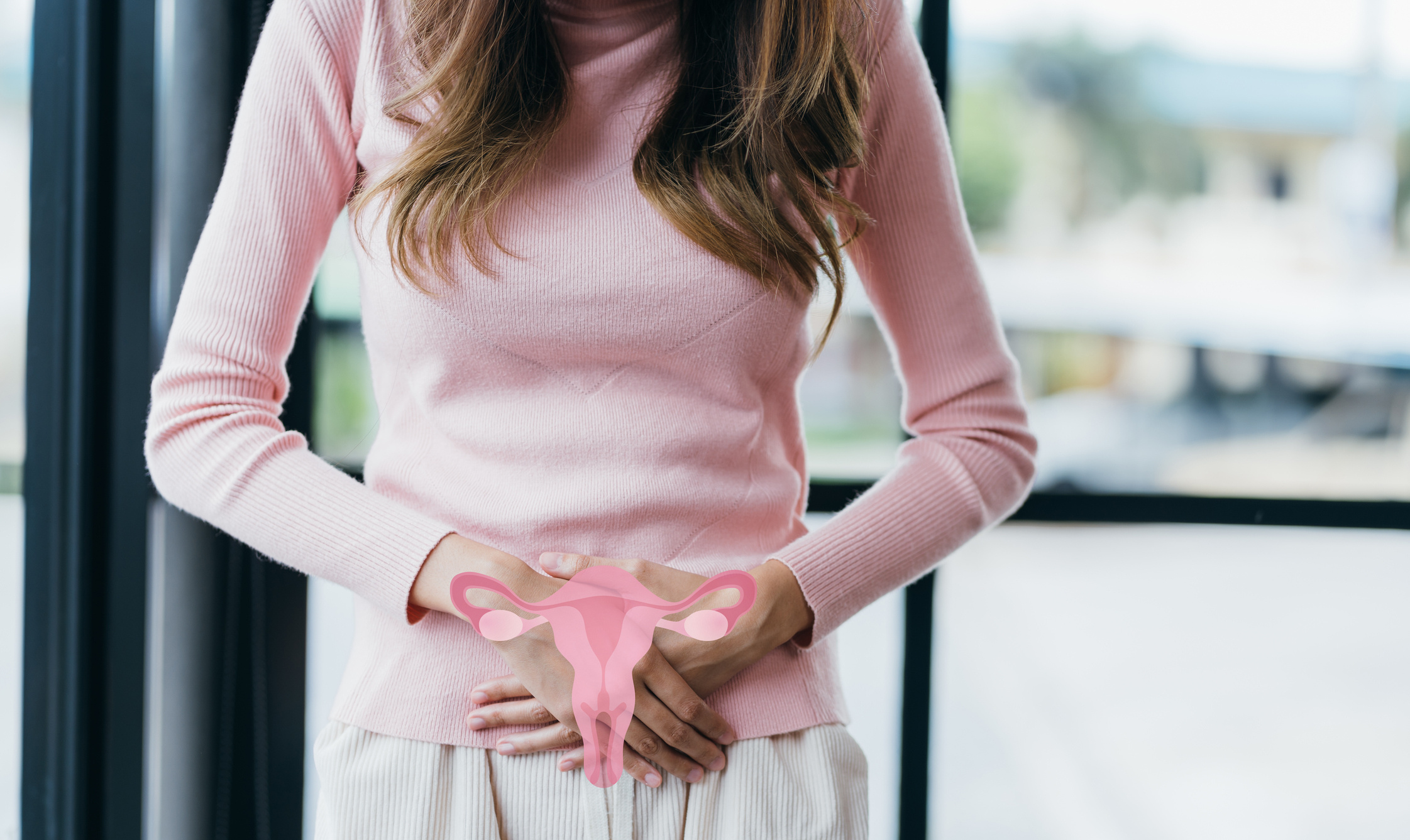

Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a double-stranded DNA virus. Approximately 630 million women worldwide are currently infected with HPV, which is transmitted through sexual contact. Unlike other sexually transmitted diseases, HPV can also be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact without direct penetration during sexual intercourse. Therefore, the protective effect of condoms is limited. The Center for Disease Control (CDC) in the USA reports that 50% of sexually active men and women will encounter HPV at some point in their lives. A population-based study in the USA found that one in four sexually active women tested positive for HPV DNA.
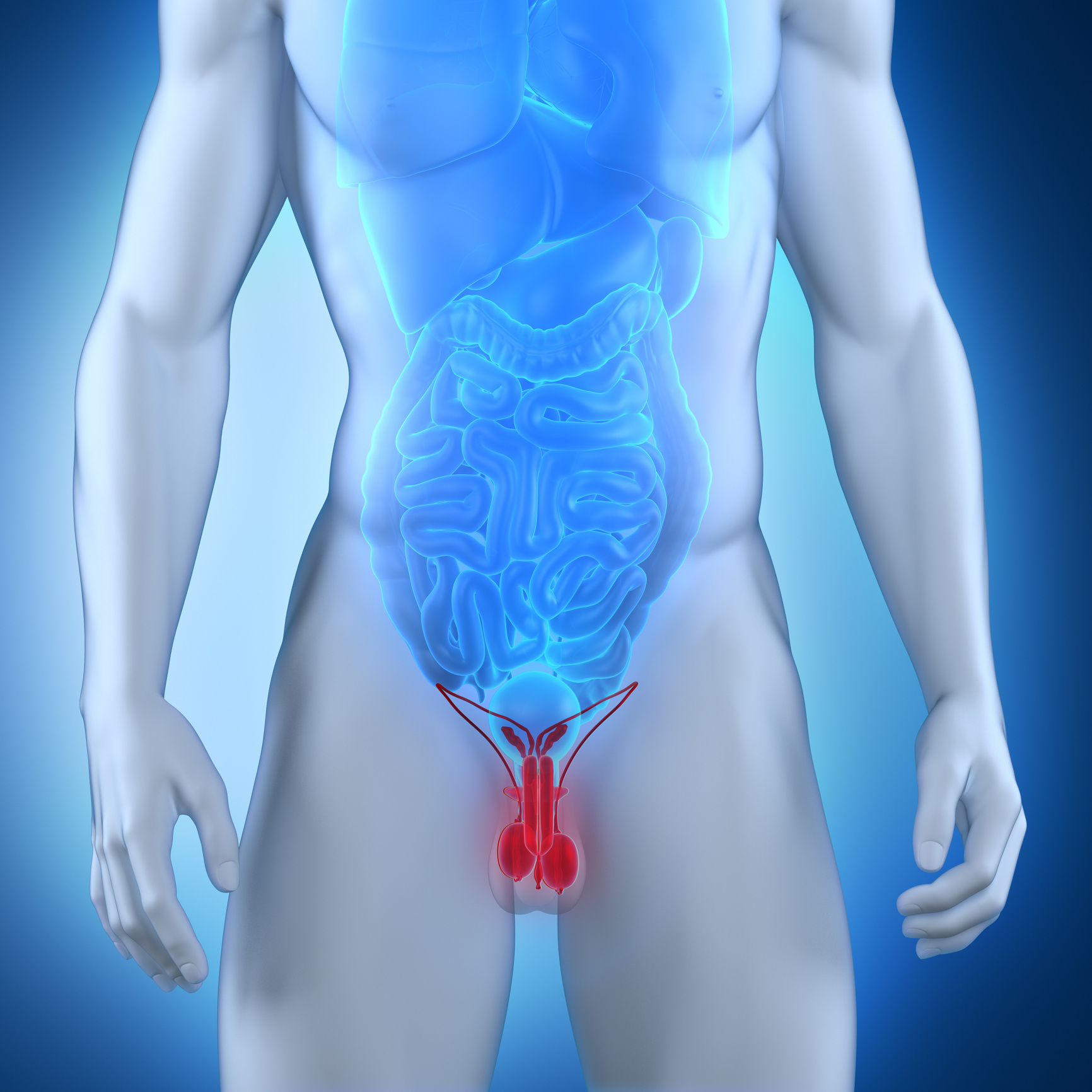
Testicles are essential organs of the male reproductive system, located in a skin sac called the scrotum behind the penis. They produce and store sperm and produce the main sex hormone, testosterone. Testicular cancer occurs due to uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cells within the testicles, forming tumors. It is one of the most common reproductive system cancers in men. Although it can progress without symptoms for a long time, it has one of the highest treatment success rates, making early diagnosis crucial.
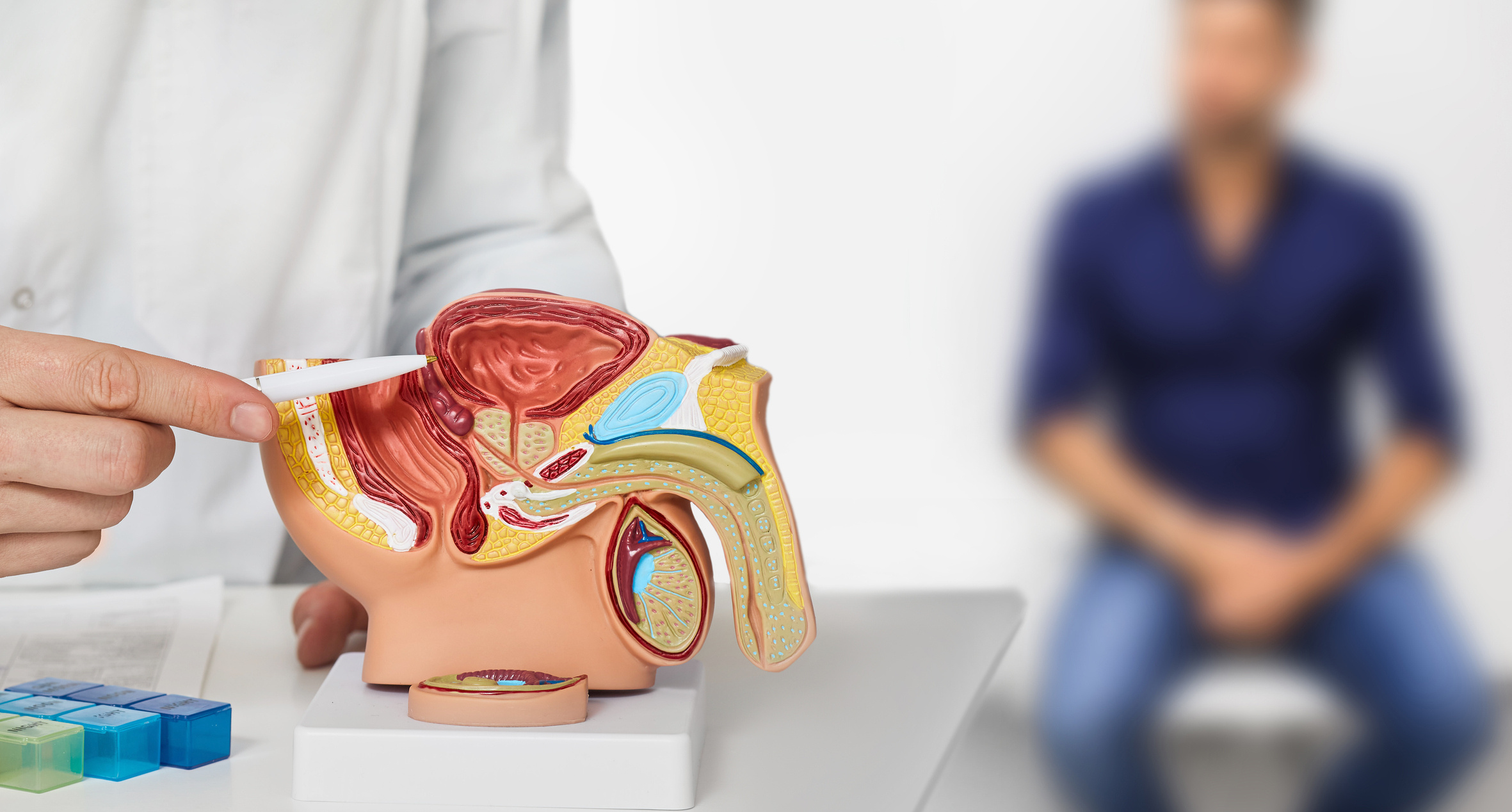
The prostate gland is an organ of the male reproductive system, located just below the bladder, with its base in contact with the bladder, and has a pyramidal structure. The prostate surrounds the prostatic urethra, which is the channel responsible for the flow of urine from the bladder. In males who have not yet reached puberty, the prostate weighs about 2 grams, but it grows with age, reaching up to 20 grams in adult males before the age of 52. The prostate is a gland that plays a significant role in male fertility. Its primary function is to produce the fluid that nourishes sperm and ensures their protection within the seminal fluid. Prostate cancer is the uncontrolled division, proliferation, and growth of cells within the prostate gland, leading to cancer. Since prostate cancer often does not show symptoms in its early stages, diagnosis can be delayed, increasing the likelihood of metastasis.
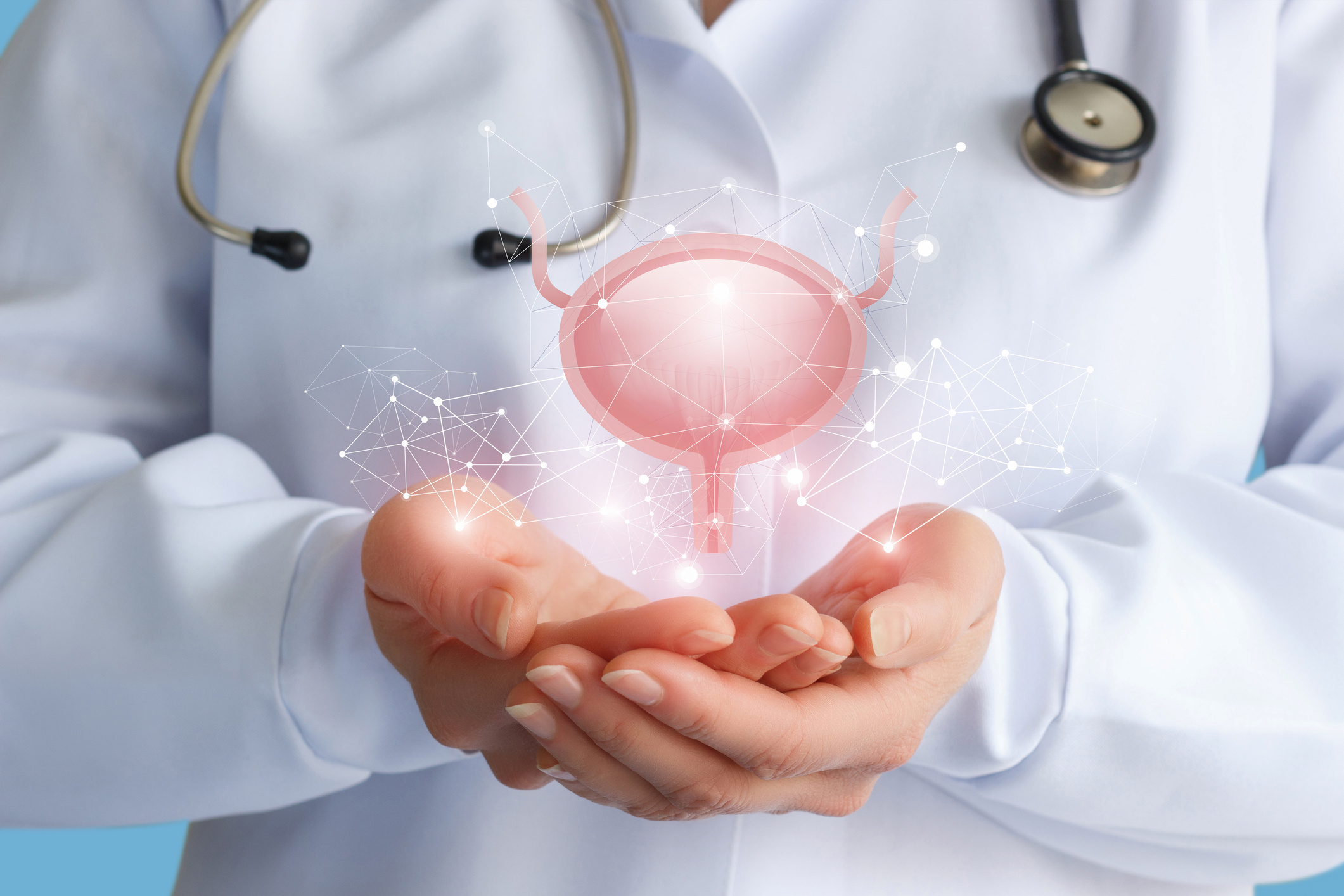

Bladder cancer is the second most common cancer occurring along the urinary tract, starting from the kidneys. Approximately two-thirds of bladder cancers are non-fatal but tend to recur, while one-third have the potential to invade muscle tissue and subsequently metastasize to the rest of the body, exhibiting a more aggressive course.
Soft tissue cancer, known in medical terms as sarcoma, is a type of malignant tumor that forms in connective tissues and is a rare type of cancer. Soft tissues are those that support, connect, or surround organs in the body, including muscle, blood vessels, nerves, tendons, and the inner lining of joints. Sarcomas can occur in childhood, young adults, and older adults. This cancer type may present as a lump or mass that can be felt in soft tissues. While sarcomas can occur anywhere in the body, they most commonly develop in the arms, legs, and abdominal region. These masses can be either painful or painless. A definitive diagnosis of soft tissue cancer is made through a biopsy, which helps determine the treatment plan. Depending on the progression of the disease, treatment options may include surgical interventions, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy.
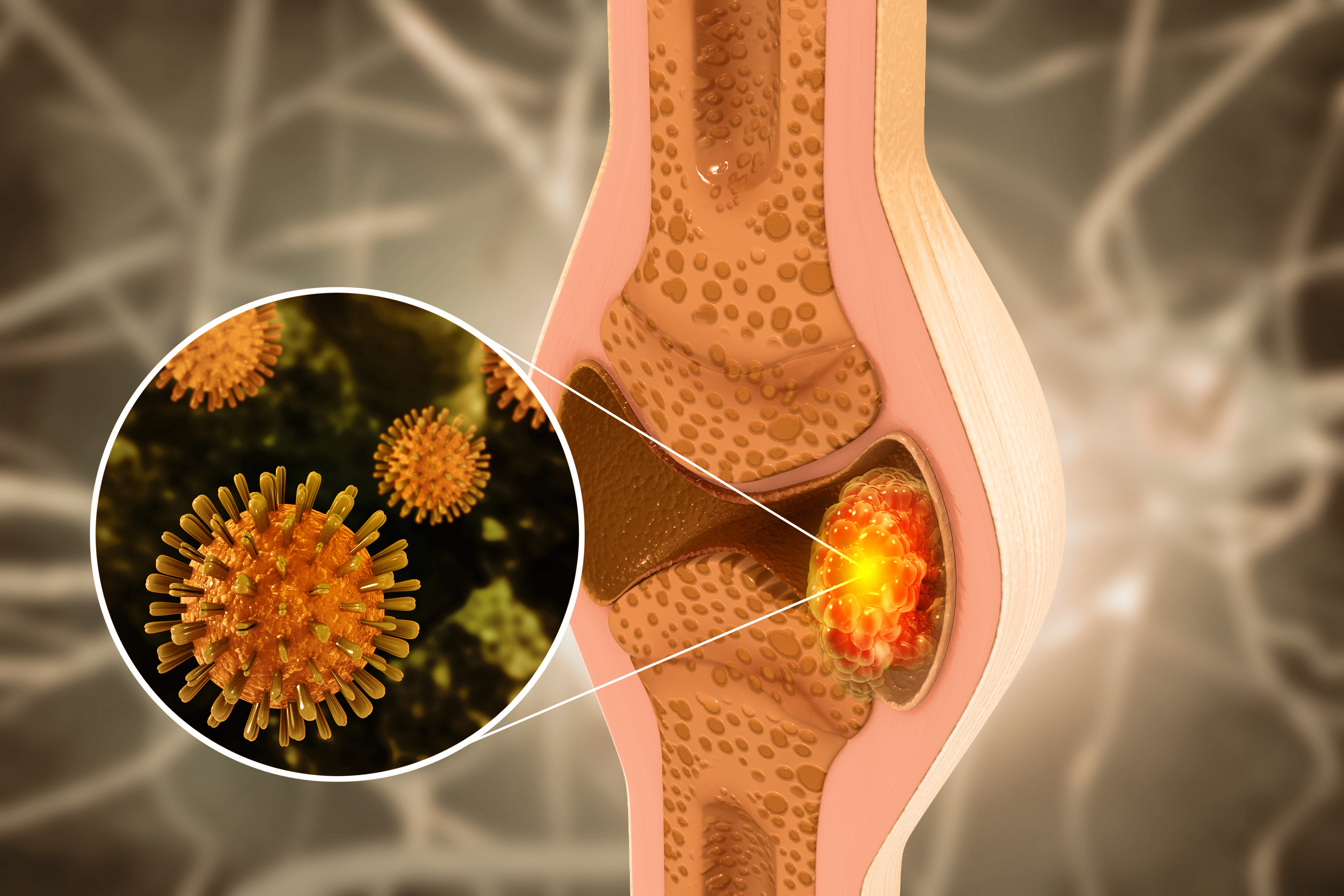
Many areas of the human body are conducive to tumor formation, one of which is the bones that cover a large part of the body. Tumors can arise from uncontrolled cell divisions occurring in the bones. If these tumors are malignant, it is referred to as bone cancer. The most common symptom of bone cancer is pain caused by the spread of the tumor or the fracture of a weakened bone due to a tumor. Additionally, there may be a feeling of stiffness and tenderness in the bone. Other symptoms such as fatigue, fever, swelling, and stumbling may also occur, but these can be caused by other conditions as well. The diagnosis of bone cancer is made through tests performed by a doctor.

The gallbladder is an organ that is part of the digestive system and plays a role in producing bile, which is necessary for fat metabolism. The gallbladder, which stores and secretes bile, is located in the upper right part of the abdomen. Due to various reasons, changes can begin to occur in the cells of the gallbladder, and these cellular changes may lead to the development of cancer. Gallbladder cancer, which can present with symptoms such as abdominal pain and bloating, is a serious medical condition that requires intervention.

Malignant tumor formations developing within the liver are referred to as liver cancer. The liver is the largest internal organ of the body. It is responsible for performing many vital functions, including the removal of various wastes from the body, absorption of various nutrients, and wound healing. Located in the upper right part of the abdominal region, the liver is also responsible for bile production.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a common subtype of head and neck cancers. These cancers differ significantly from other head and neck malignancies in terms of their etiology, epidemiology, histopathology, biological behavior of the disease, and treatment. Therefore, nasopharyngeal cancers should be considered separately from other head and neck malignancies. This type of cancer is difficult to diagnose early, and its treatment typically involves radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
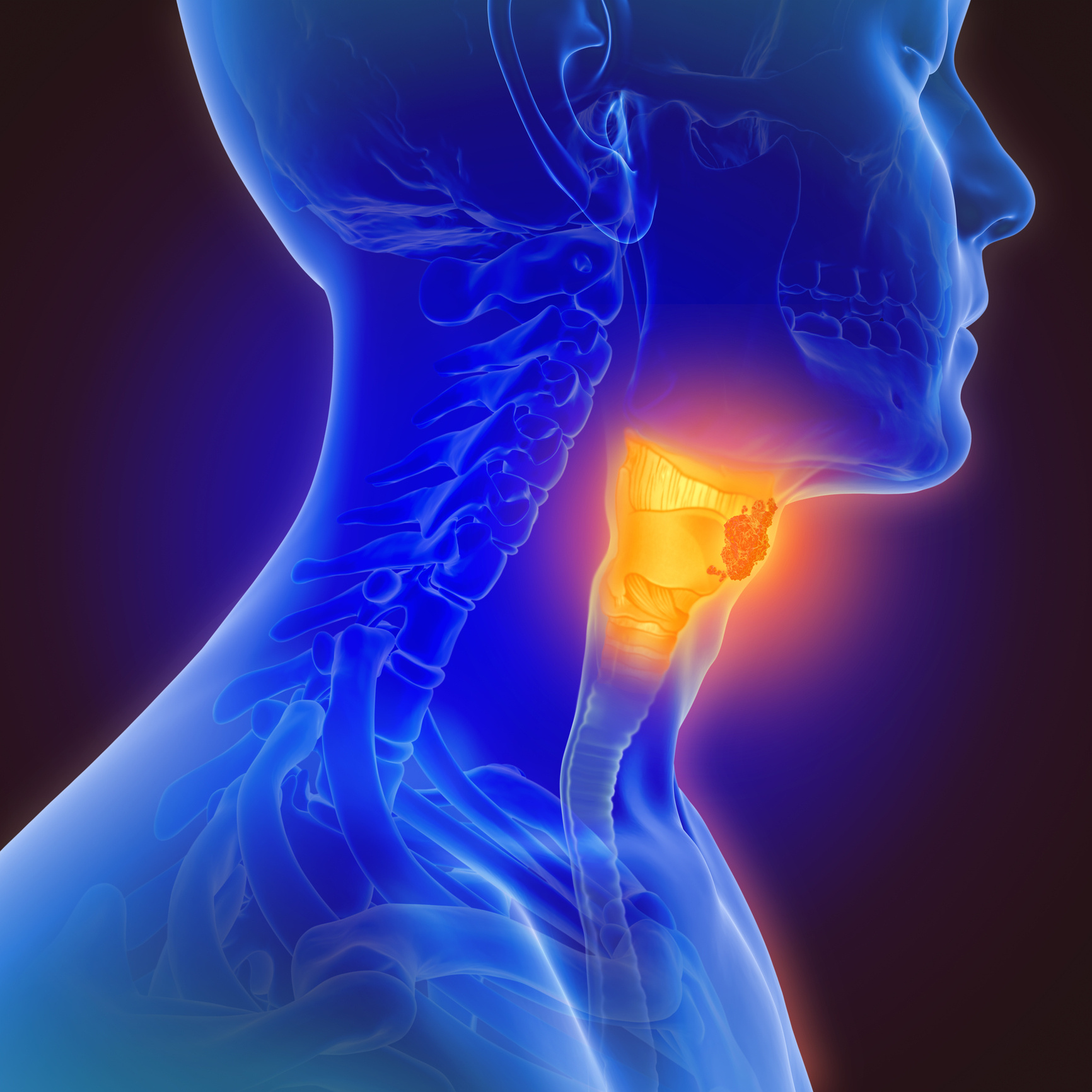
The pharynx, or throat, is located behind the nasal and oral cavities. Its upper part is connected to the nasal cavity (nasopharynx), while its lower part (hypopharynx) continues to the esophagus. Throat cancers include cancers of the base of the tongue, uvula, tonsil tissue, and the back walls of the throat. Oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers are considerably rarer than nasopharyngeal cancers. Worldwide, an estimated 123,000 new cases of oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers are diagnosed annually.

Tongue cancer is one of the types of oral cancer that develops from the cells found in all areas of the tongue. This condition can lead to the formation of tumors, growths, and lesions in the mouth. Tongue cancer is divided into different subtypes depending on which part of the tongue it develops in. These subtypes have their own specific symptoms. The most common symptom of tongue cancer is the presence of non-healing sores on the tongue. While tongue cancer is more commonly seen in older individuals, there has been a recent increase in cases among younger and middle-aged individuals. With early diagnosis and treatment, tongue cancer can be managed and treated effectively.
Head and neck cancers refer to the uncontrolled and abnormal growth of cancer cells in the head and neck area of the body. Early diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancers are crucial. While these cancers can be treated successfully in many cases, they can also cause permanent damage in some situations. To prevent such damage, various treatment methods can be applied to eliminate the cancer cells or halt their progression.

Oral cancer is a global health problem and ranks second in frequency among head and neck cancers in our country, with developed countries being the most affected. As with many conditions, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for this type of cancer. Oral cancer, which is classified under head and neck cancers, refers to cancers that develop in any part of the mouth area, including the inside of the cheeks and gums. This malignant tumor, also known as oral cancer, typically originates from the squamous (flat) cells in the mouth, tongue, and lips. To learn more about this cancer type, you can continue reading the article.
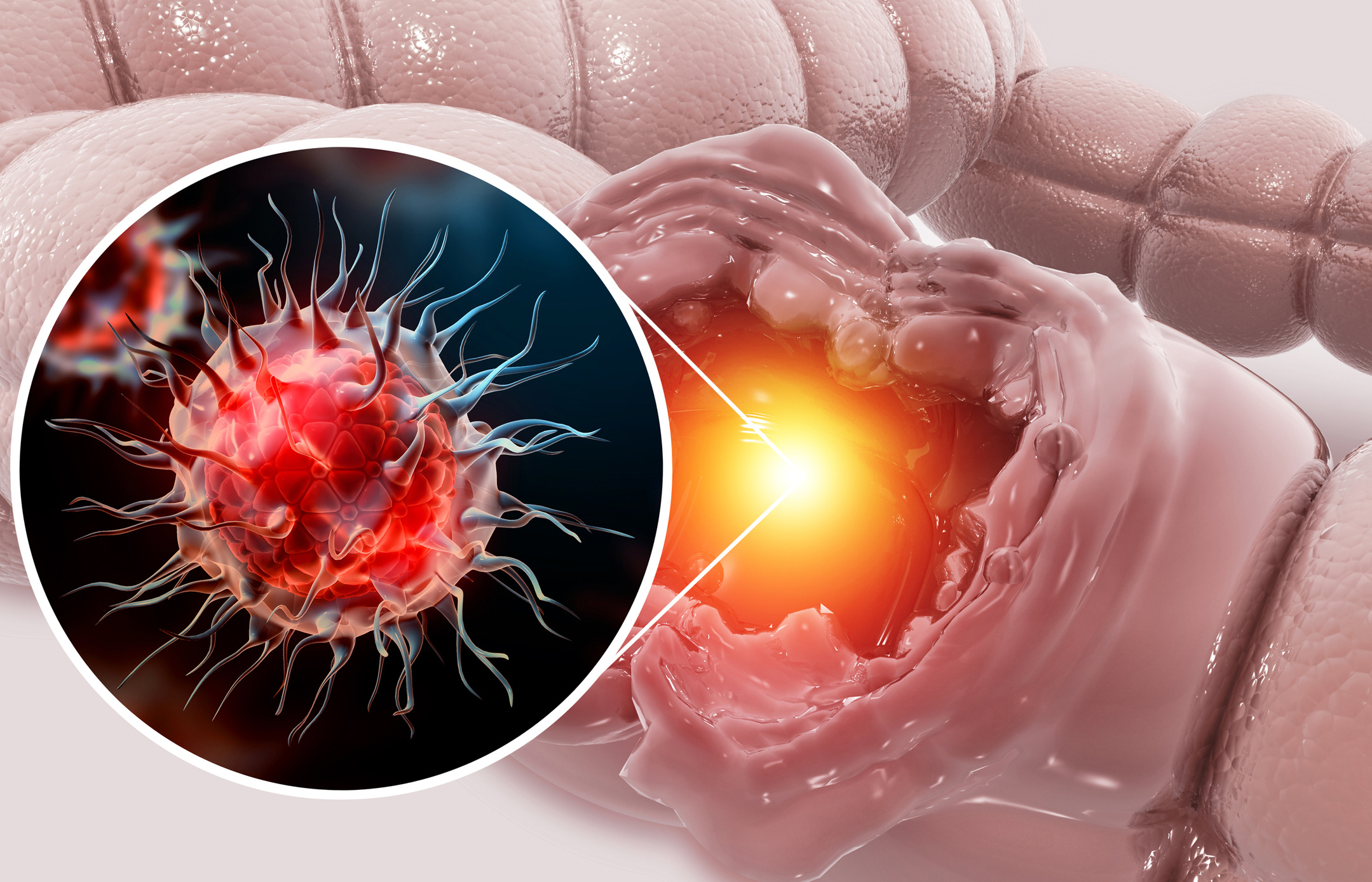
The rectum is the last 15 cm of the muscular channel called the colon, which is an important part of the digestive system. Tumor cells that develop in this 15 cm area may lead to rectal cancer once they reach a certain number. It is a type of cancer with a high mortality rate, which is why early diagnosis and treatment are critical. Rectal cancer may develop without symptoms in some cases. Some patients may experience symptoms such as rectal bleeding, diarrhea, constipation, and unexplained weight loss. A family history of rectal cancer and certain hereditary disorders may increase the risk of rectal cancer. Treatment procedures may vary depending on the stage of the cancer. The general treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
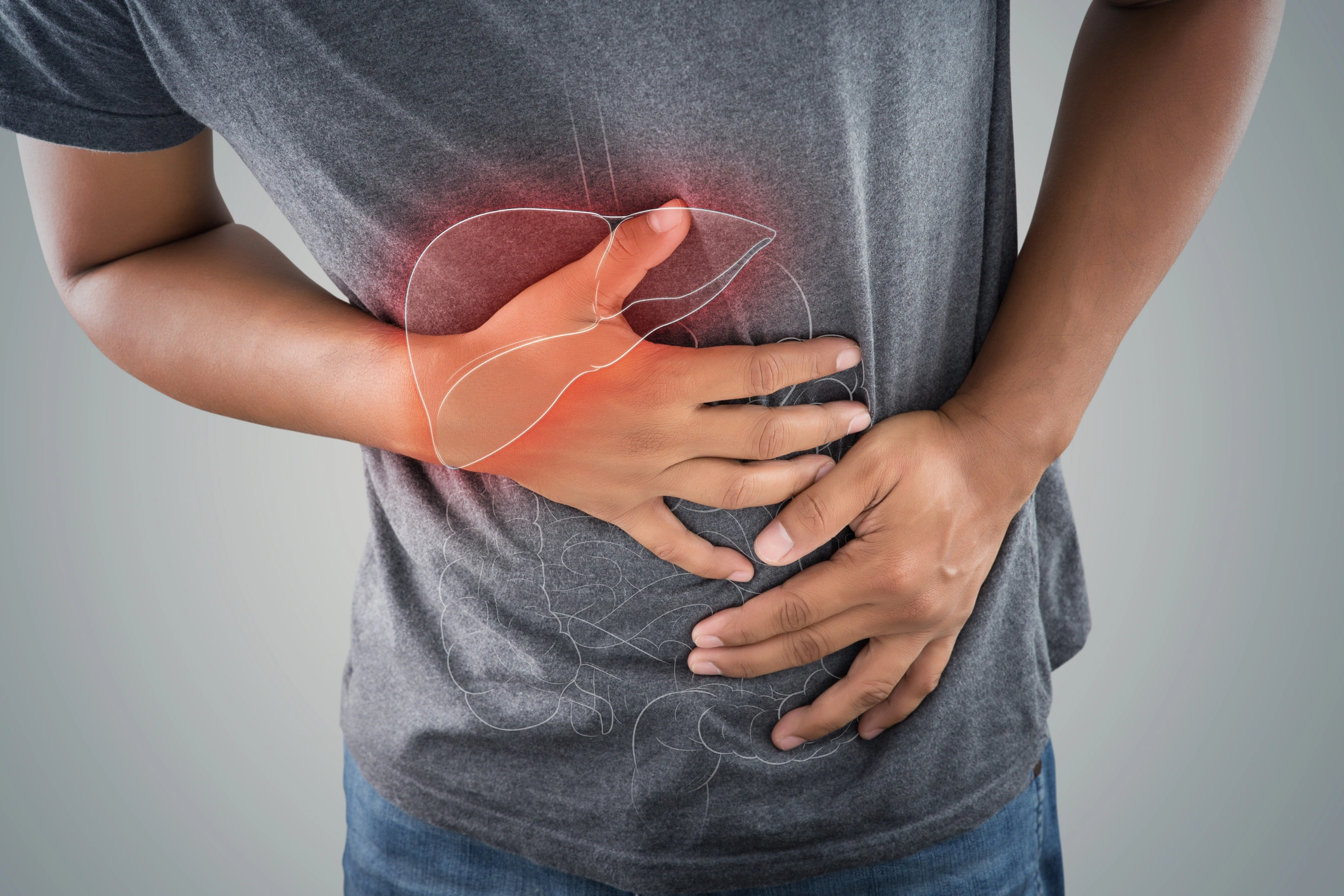
Pancreatic cancer is a condition that affects the pancreas, an organ located in the abdominal region that helps with digestion. Symptoms may include nausea, bloating, fatigue, jaundice, and loss of appetite. Treatment methods include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Due to the difficulty of detecting the disease in its early stages, it can lead to serious complications.
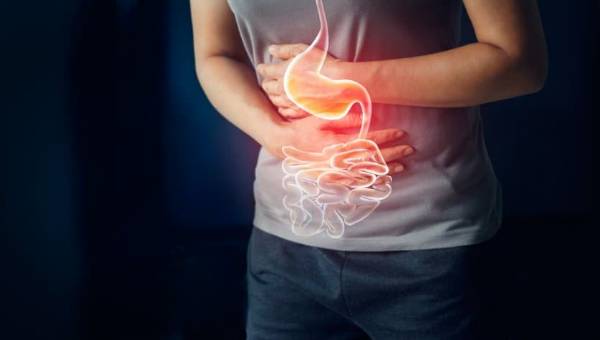
Stomach cancer is a type of cancer that occurs due to the uncontrolled growth and multiplication of cells lining the surface of the stomach. It can form at the junction of the esophagus and stomach or in the body of the stomach. Compared to other cancers, it develops more slowly.
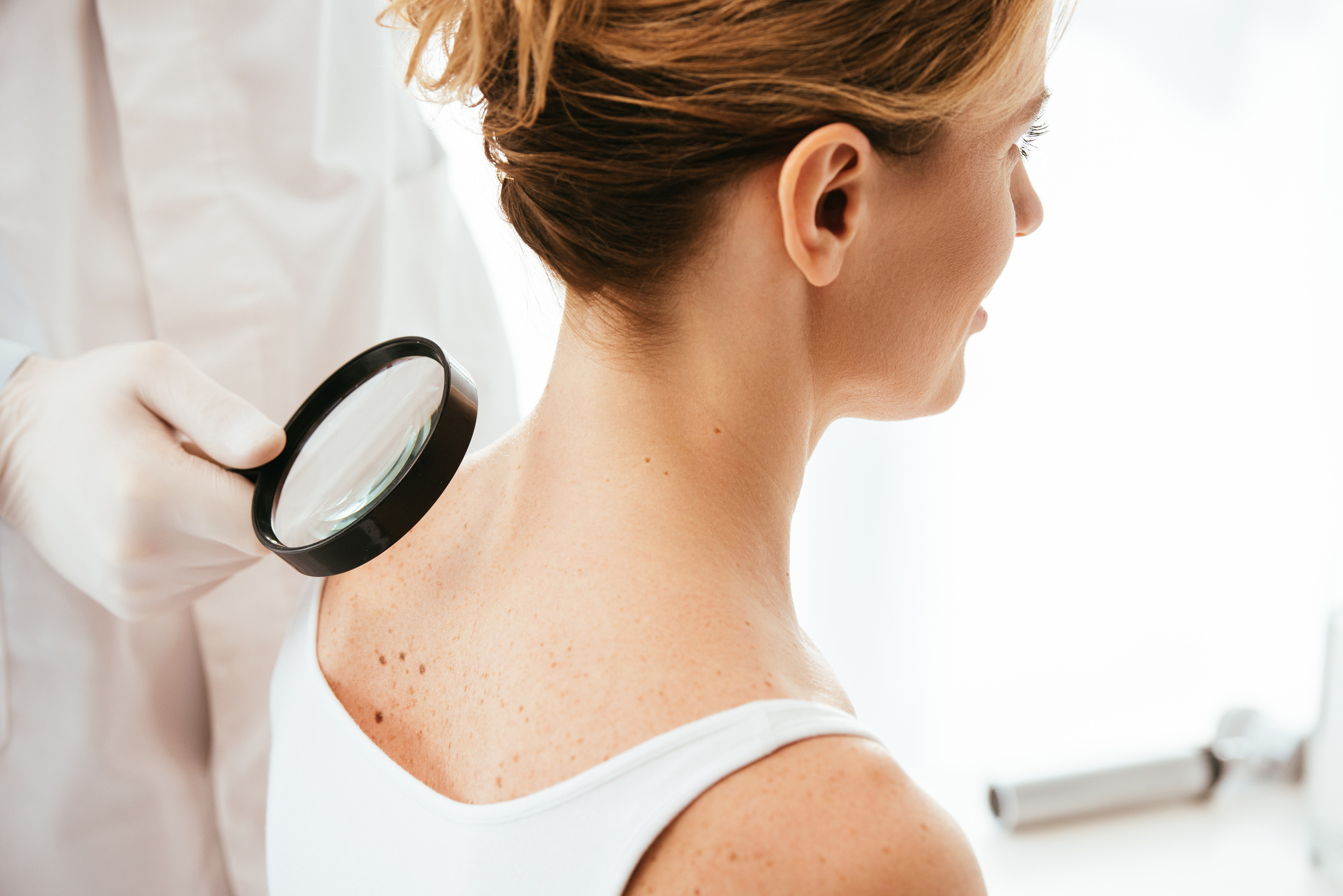
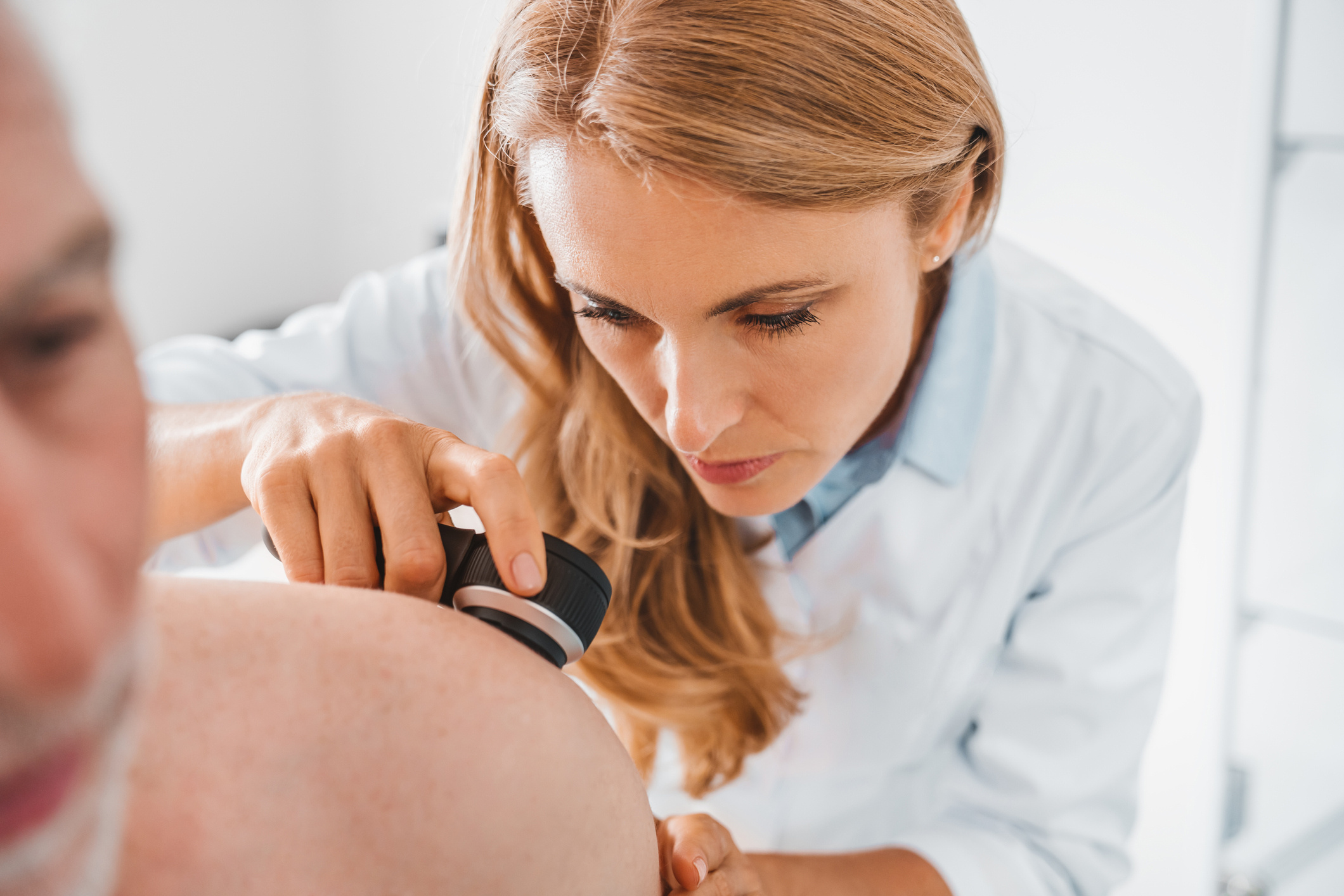
Skin cancer, contrary to popular belief, is a common type of cancer. Research has shown that nearly one in five people will develop skin cancer at some point in their lives (1). Moreover, if diagnosed early, the disease can be completely treated. Common treatment methods include excision, cryotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation, and Mohs surgery. Appropriate treatments can be applied based on the type or stage of the disease. In some cases, a combination of several treatment methods may be used. Early diagnosis is crucial for complete treatment, so it is important to pay attention to any changes in the skin. To avoid skin cancer, it is important to have a dermatology check-up at least once a year.
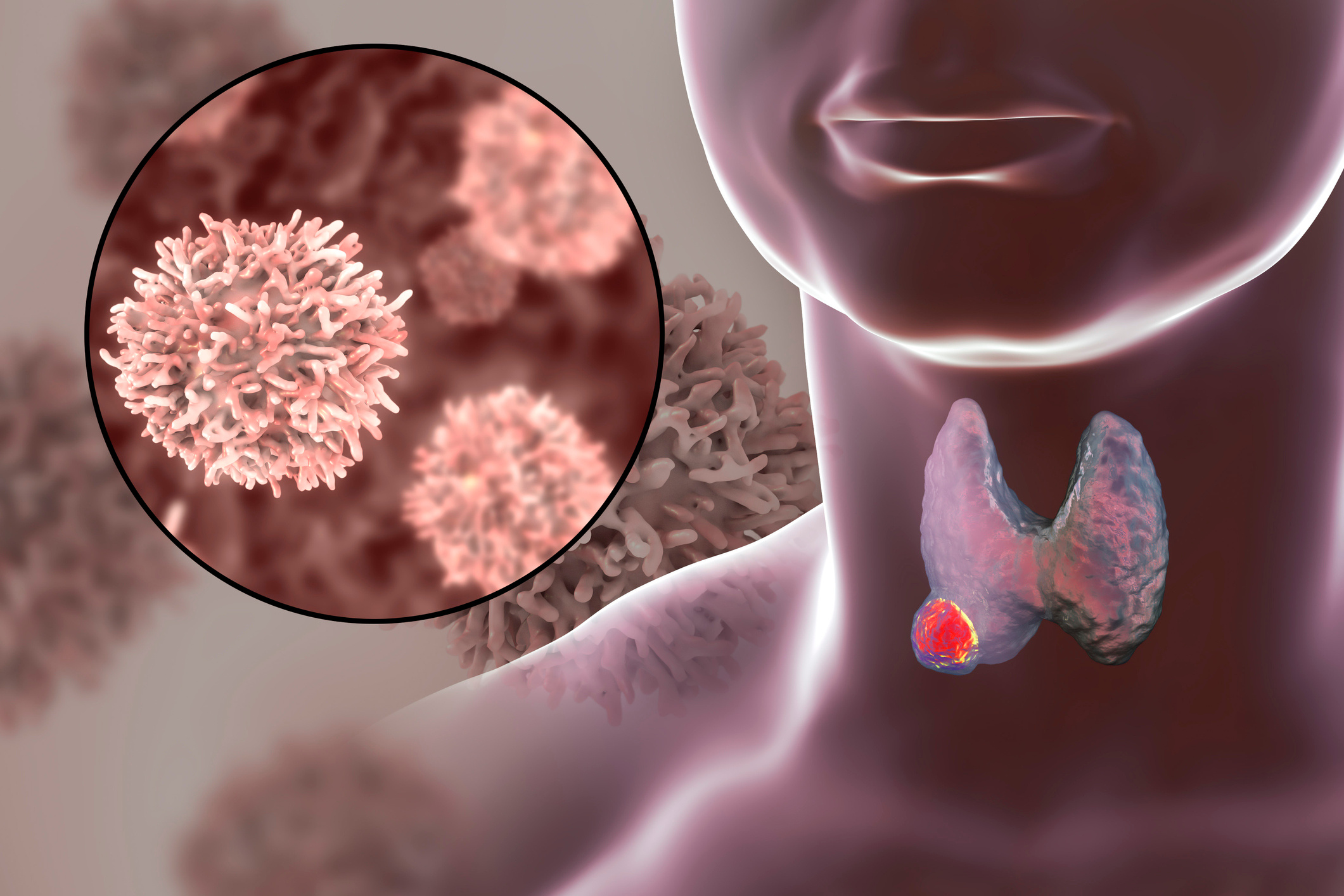
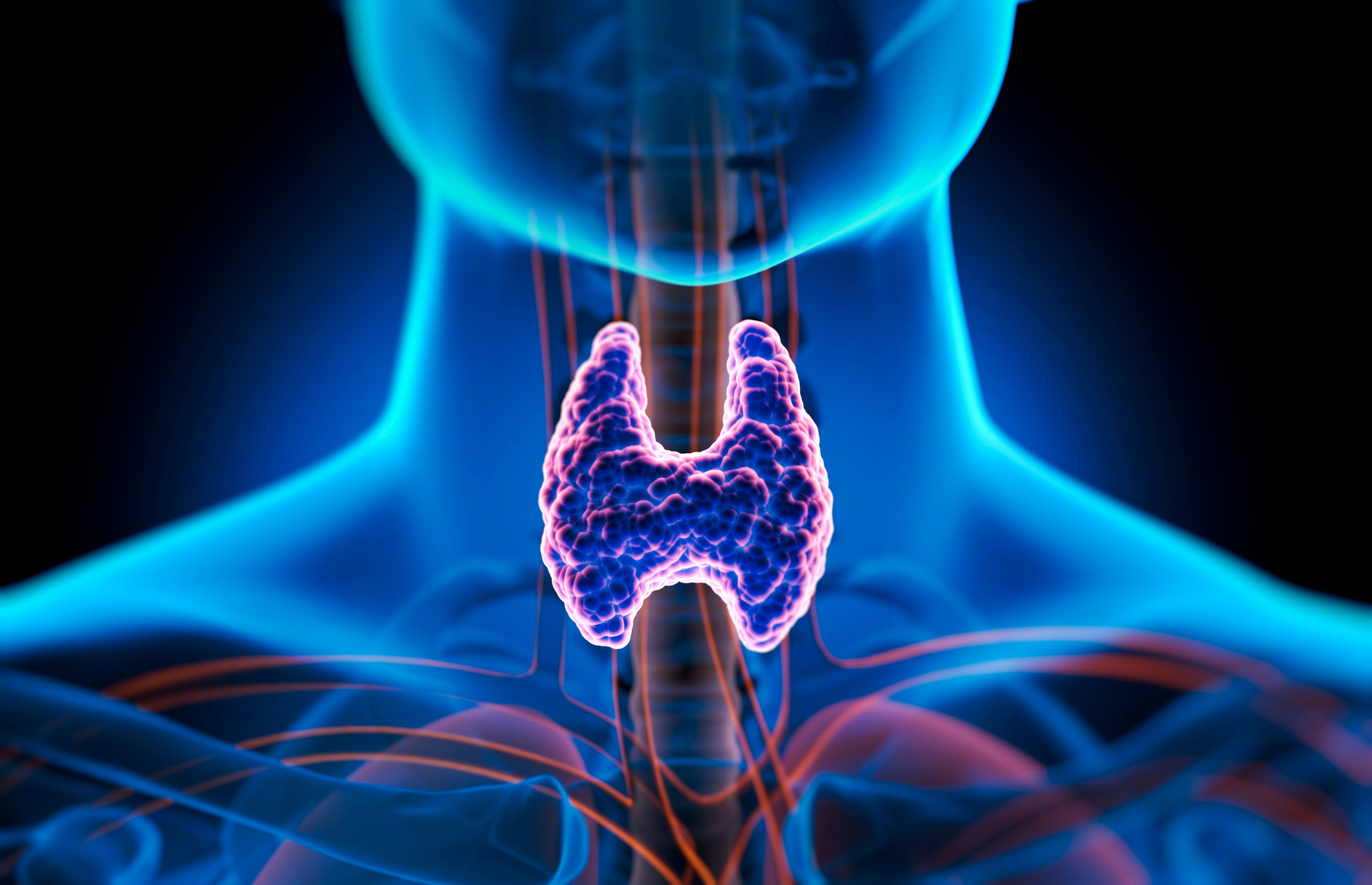
Thyroid cancer is an uncontrolled cell growth that starts in the thyroid gland and has many types. While most types grow slowly, some can be aggressive. This type of cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages; however, as the cancerous tissue grows, it can lead to symptoms such as swelling in the neck, changes in voice, and difficulty swallowing. Thyroid cancers account for approximately 1% of all cancers【1】. In recent years, the incidence has increased particularly among the female population. Imaging methods may be used during the diagnosis stage. Most thyroid cancers can be treated with various procedures, and the types of cancer that respond best to treatment are small tumors in the early stages.

Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. It accounts for 24% of all female cancers and 15.5% of cancer deaths. It is reported that 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives. Rarely, breast cancer is also seen in men, with 1 man diagnosed for every 100 women. The incidence of breast cancer has been found to increase every year.
The skin is an organ that protects the body against external factors such as heat, light, microorganisms, and injury. Acting as a vital barrier for organs, the skin helps maintain body temperature, receive various signals from the environment, and provide immune system defense. The thickness and texture of the skin can vary among individuals. However, all humans have skin composed of three layers. The outermost layer of the skin is the epidermis, which contains melanocytes that give color to the skin. Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, which houses sebaceous glands, hair follicles, nerve endings, and sweat glands. The innermost layer, the hypodermis, is a fatty tissue where body fat is stored. Each layer can have different functions. The sebaceous glands in the dermis are small glands that help reduce fragility by covering hair follicles. The lumps that occur due to the excessive growth of cells in this fatty tissue are called lipomas. Lipomas can form in any area where fat cells are present, and they are generally benign and usually harmless. Known as "lipomas," these lumps are painless, mobile, and fatty. They typically occur in adults aged 40-60 years. The formation of cancerous lipomas is rare and is referred to as "liposarcoma." Dermiste bulunan yağ bezleri kıl köklerini kaplayarak kırılganlığı azaltmaya yardımcı olan küçük bezlerdir. Bu yağ dokusundaki hücrelerin aşırı şekilde büyümeleri sonucu oluşan yumrulara yağ bezesi denir. Yağ hücrelerinin bulunduğu her bölgede oluşabilen yağ bezesi iyi huylu ve genellikle zararsızdır. “Lipom” olarak bilinen yağ bezeleri ağrısız, hareketli ve yağlı yumrular şeklindedir. Genellikle 40-60 yaş yetişkinlerde görülebilir. Kanserli lipom oluşması nadirdir ve “liposarkom” olarak adlandırılır (1, 2).


Lymphoma is a general term that describes cancers originating from the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. Lymphomas are commonly known as lymph node cancers, but the disease can also occur in organs without involving the lymph nodes.
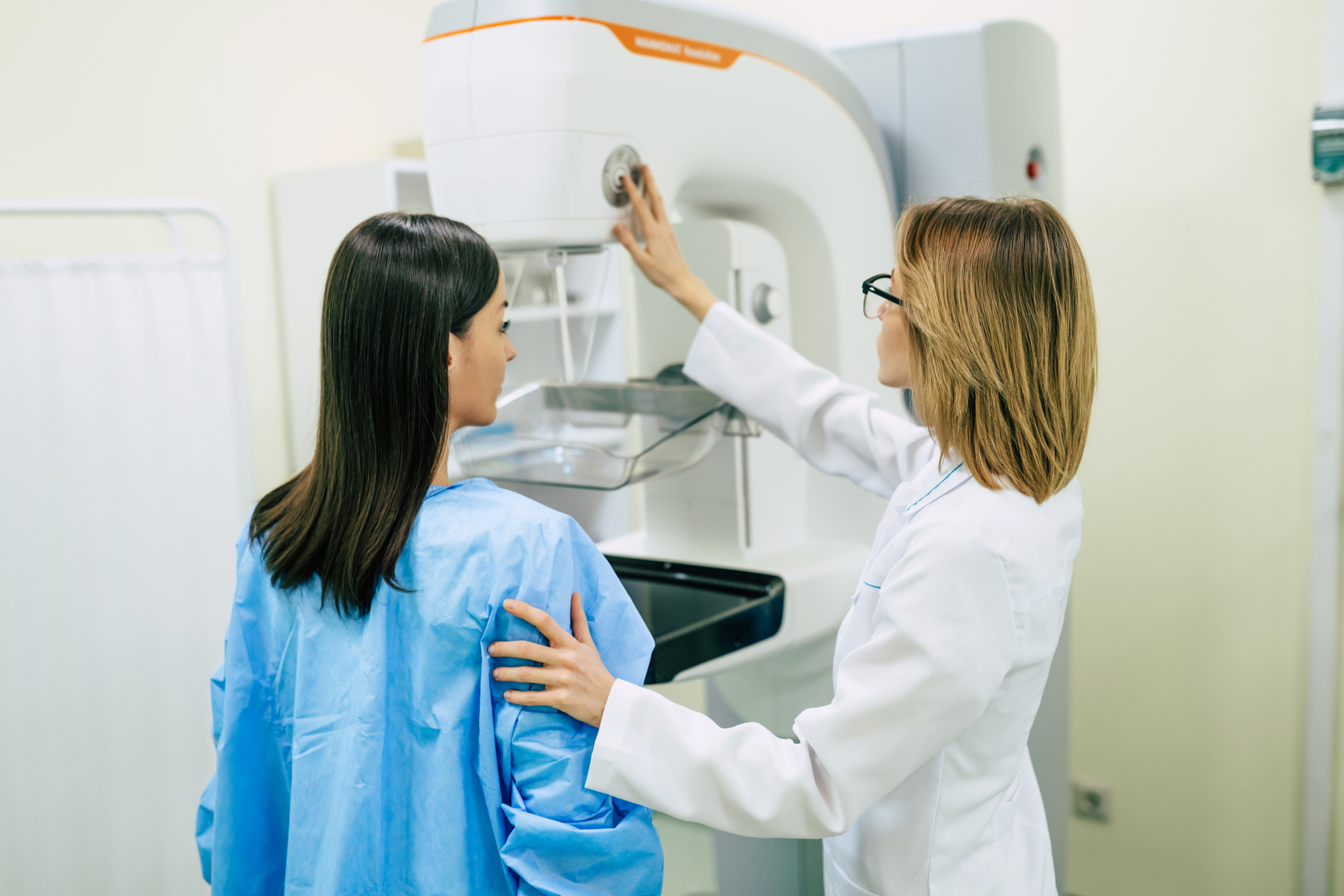
The high prevalence of breast cancer, its increasing frequency, the possibility of treating it in its early stages, and the ability to diagnose it at an early stage under current conditions all increase the importance of screening methods for breast cancer.
Certain types of cancer are more prevalent in childhood. Early detection of these cancers is more likely when families are aware of the symptoms. Cancers detected early are easier to treat and have less chance of spreading.
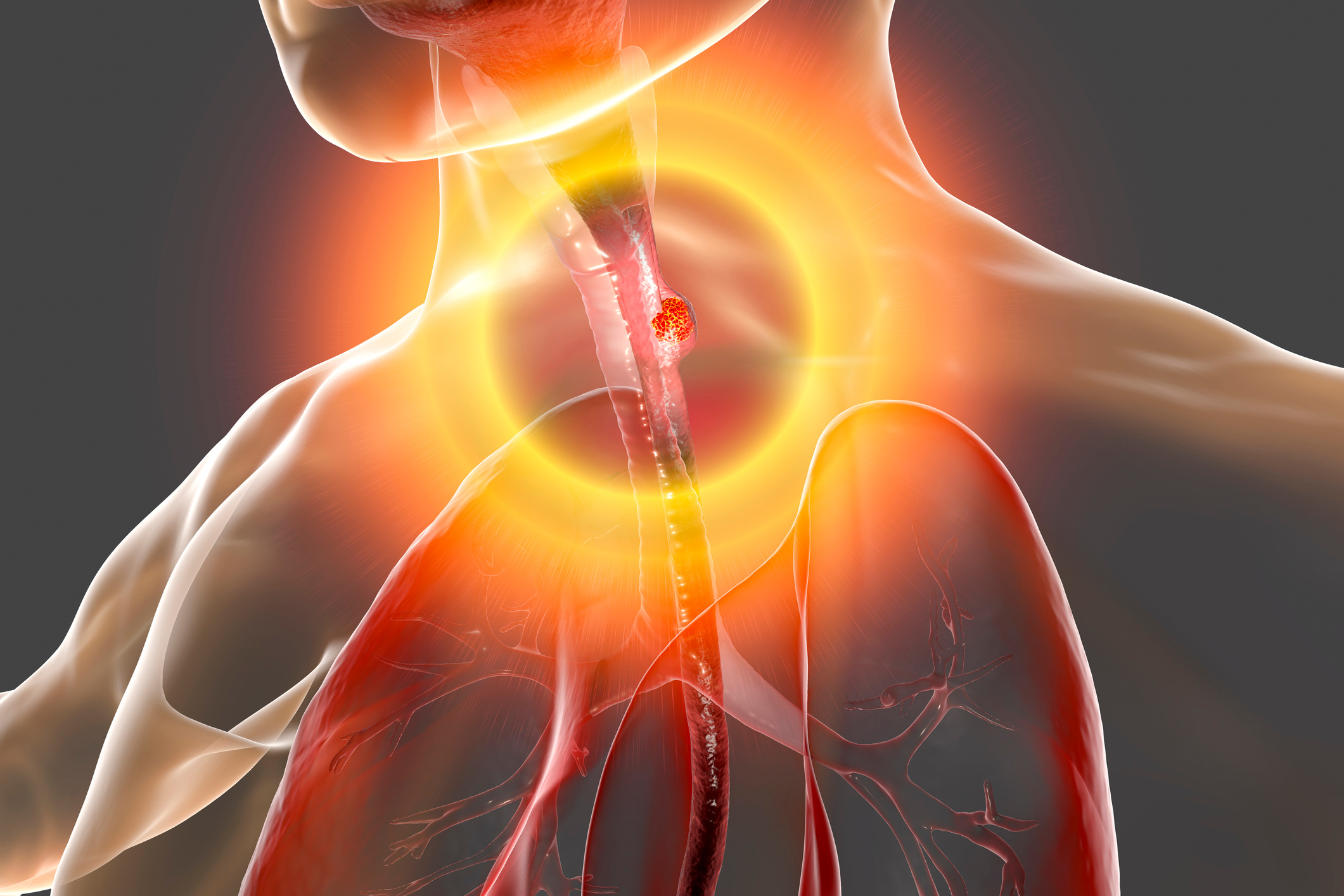
Esophageal cancer is a condition that affects the esophagus, the long, muscular tube that carries food from the throat to the stomach. Symptoms are often not noticeable until the cancer has spread, making early detection challenging. The most common types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma typically develops in the upper part of the esophagus, while adenocarcinoma usually occurs in the lower part. Symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, pain, weight loss, indigestion, and esophageal blockage. Risk factors include chronic reflux disease, obesity, and certain dietary habits. With early diagnosis, doctors can successfully intervene with surgery and other treatments
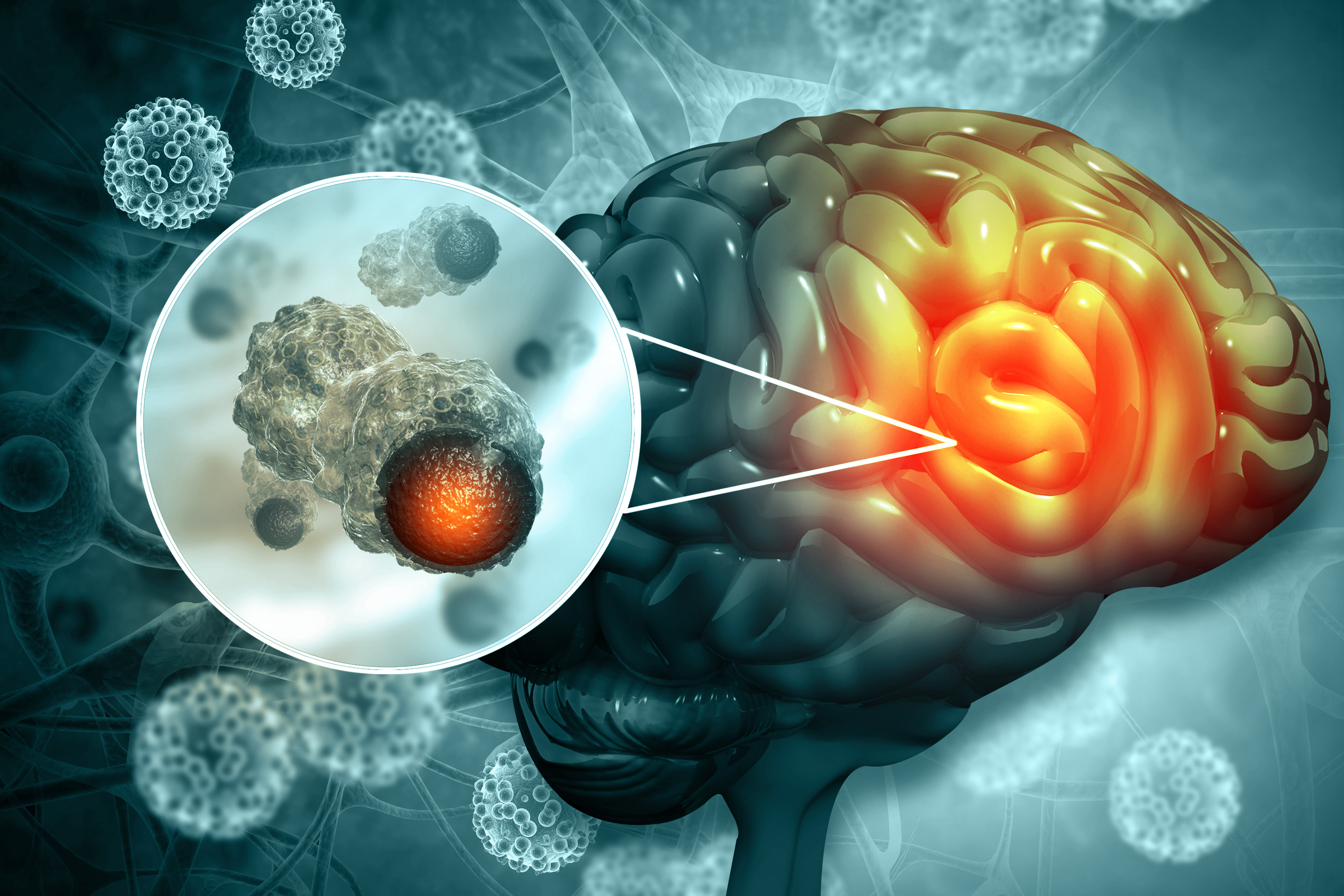
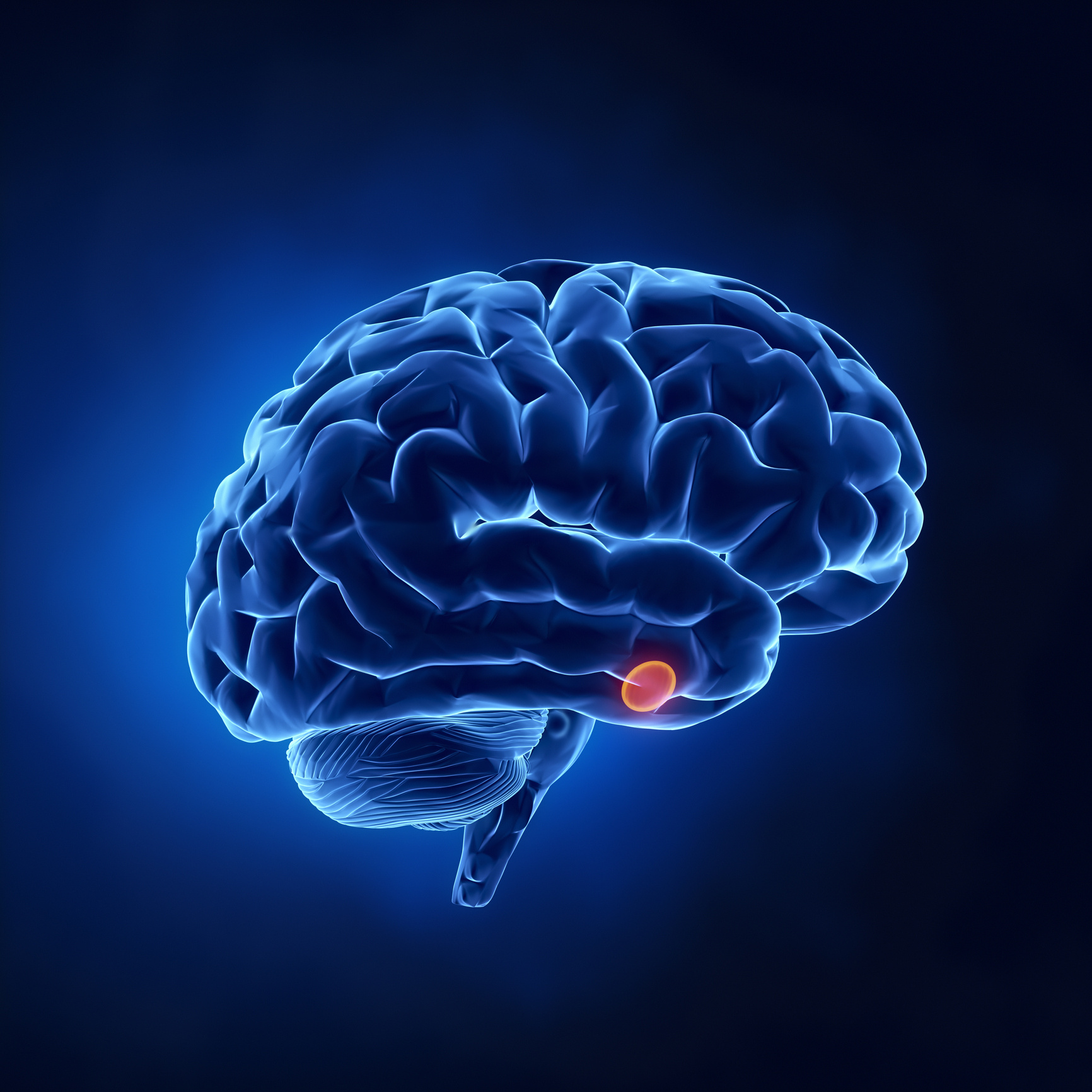
Brain cancer is the rapid and uncontrolled multiplication and growth of malignant tumor cells in the brain. The cells responsible for brain cancer have the ability to self-renew. Brain tumors can occur in the pituitary and pineal glands, the membrane on the surface of the brain, and the nerves. Secondary tumors, which originate in other parts of the body and spread to affect the brain, are more common than primary brain tumors that arise directly in the brain. The most commonly observed cases of brain cancer originate from secondary brain tumors. In 2022, it was reported that more than 1,900 people, with an average age of 59, were diagnosed with brain cancer worldwide.
21 Ağustos 2023 Pazartesi
What is Smart Drug in Cancer? How Should Smart Drugs Be Used?

500 times read
Featured Cancer Articles


