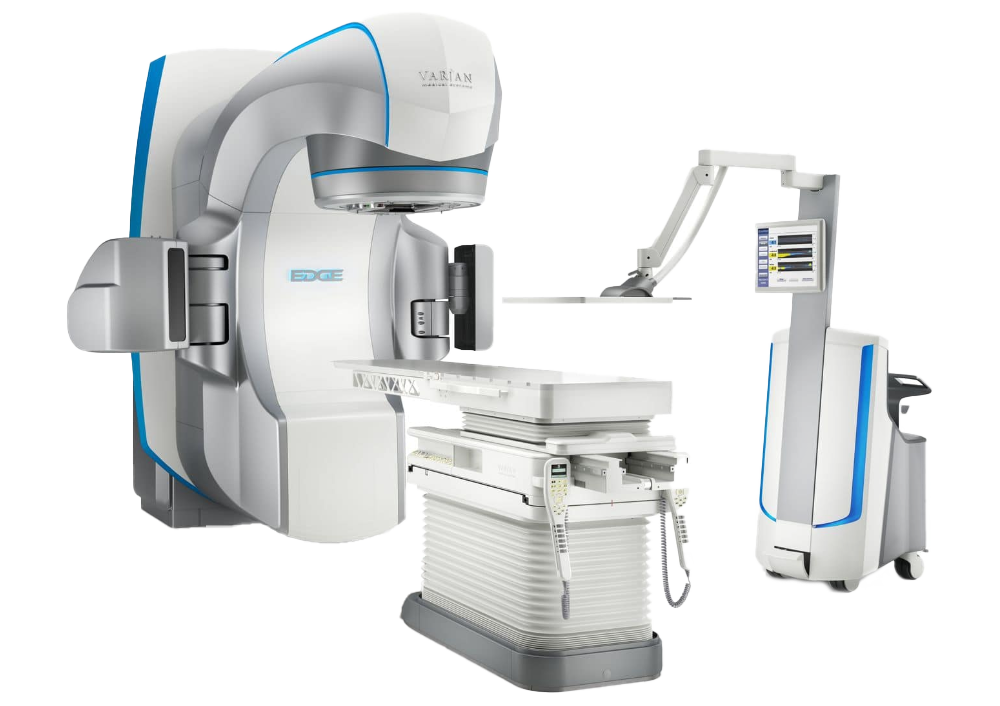
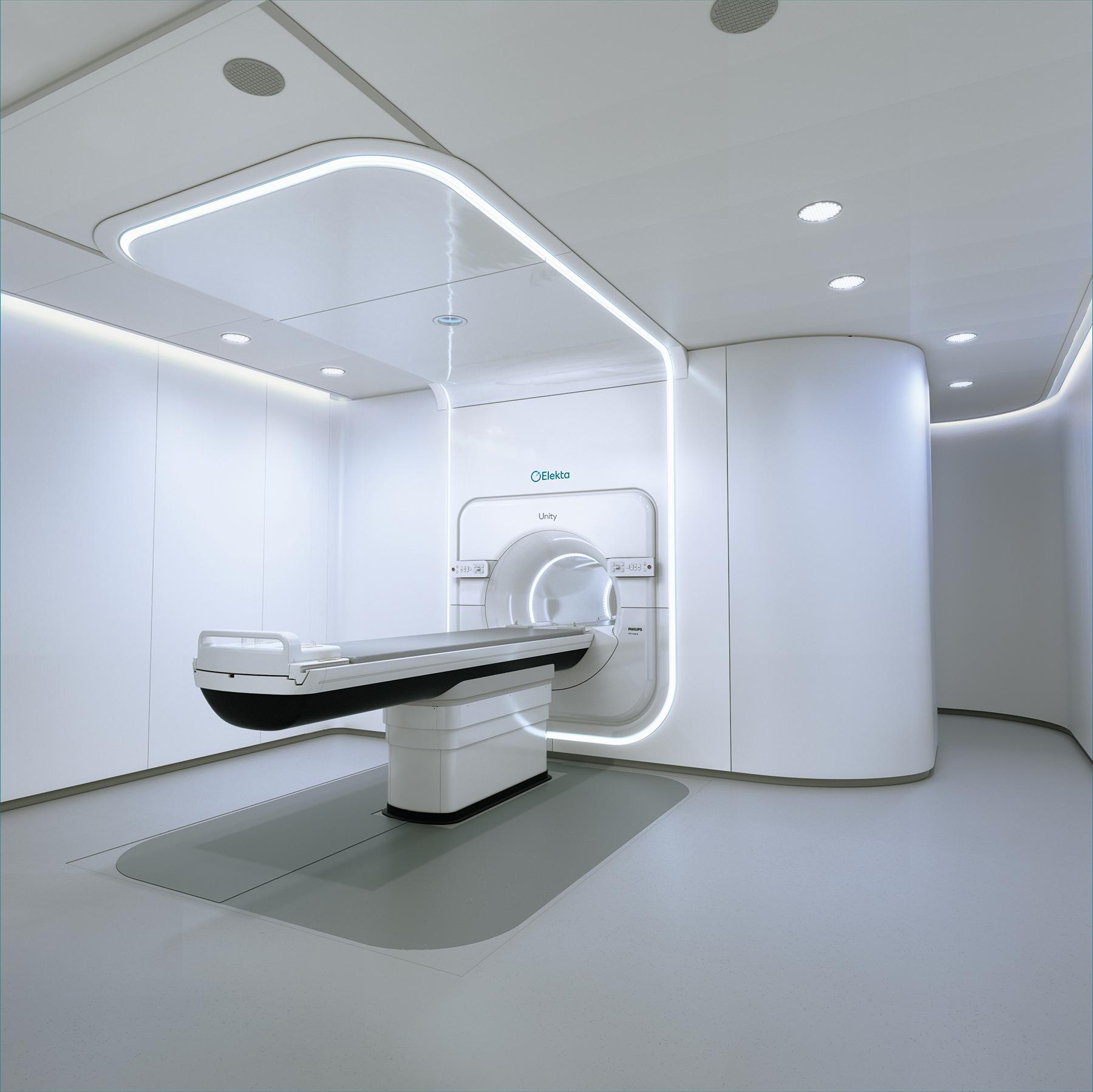
Varian Edge
New Device in Radiosurgery: VARIAN EDGE
In radiotherapy, the aim is to control or completely destroy cancerous tissues using high-energy radiation beams while also protecting the healthy organs surrounding the cancerous tissue from radiation. The Varian Edge, which was first used in Turkey at Anadolu Health Center, is one of the radiotherapy devices that combines the most advanced technologies in cancer radiotherapy.

Since June 2018, the Varian Edge radiosurgery system has been used for patient treatments at Anadolu Health Center. It particularly integrates the most advanced technologies for stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery (SRT, SRS). The patient can continue their normal life after receiving their session on the specified day and time, as the treatment does not affect daily living and is performed on an outpatient basis.
Precision Below a Millimeter
The key point of the Varian Edge system is precision and treatment accuracy. Thanks to the technologies within the Edge system, radiotherapy and radiosurgery treatments can be applied with precision and accuracy below a millimeter to tumors in any part of the patient's body, such as the lungs, brain, spinal cord, pancreas, and prostate.
With the Edge system's different levels of X-ray energies, therapeutic radiation doses can be easily delivered to any area of the patient's body. The real-time digital architecture of the Edge system ensures high-level synchronization of imaging, patient positioning, motion tracking, beam shaping, and dose delivery units. Intracranial or extracranial tumors can be tracked in real-time, and calculated patient position corrections can be easily applied through a six-dimensional movable patient bed.
Treatment Accuracy Enhanced by Respiratory Tracking System
The respiratory tracking system allows for more accurate treatments by eliminating uncertainties caused by tumor movements with respiration. The HyperArc technology of the Edge system makes stereotactic brain radiosurgery applications more practical and faster with different table angles.
Features of the Varian Edge
The Edge System is a device that can apply multiple treatment techniques such as IMRT, VMAT, SRS, and SBRT on the same platform.
The entire system operates with mechanical precision below 1 millimeter. Thus, it can perform tumor irradiations with millimeter accuracy while also protecting surrounding healthy organs with the same precision.
With Flattening Filter Free (FFF) energies, dose rates are increased by 4 times in high energies and 2 times in low energies compared to classical applications, allowing for faster patient treatment. Thus, irradiation times can be reduced to 2-4 minutes.
The imaging, positioning, and treatment unit systems are controlled digitally and integrated as a complete platform.
With advanced imaging equipment, anatomical structures and tumor placement can be visualized before the treatment starts, allowing for image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) application.
The 0.25 cm thick HD 120™ MLC beam shaper allows for precise irradiation of even very small tumors.
The six-axis movable patient bed helps in more accurate positioning of the patient.
The RPM system helps eliminate uncertainties caused by tumor movements during irradiation by considering the respiratory signal of the patient.
The Optical Surface Monitoring System (OSMS) allows tracking of the patient's head movement during stereotactic brain irradiation using a non-ionizing radiation method.
The HyperArc technology of the system enables stereotactic brain radiosurgery treatments with different table angles (non-coplanar) to be applied more practically and quickly.
Main treatment techniques with Varian Edge™ include:
Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT):
IGRT is the process of positioning the patient by taking digital radiographic images of the patient before and, if necessary, during each irradiation session using integrated imaging equipment, and checking the anatomical structures and tumor placement against planning tomography images. In the Varian Edge system, treatments are carried out under guidance from the obtained 2D KV or MV and 3D CBCT radiographic images, ensuring patient positioning accuracy.
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT):
IMRT is an advanced and complex radiotherapy technique. It ensures that maximum dose reaches tumors near vital structures while also protecting the surrounding healthy tissue to a significant extent. In this technique, the intensity of the radiation is adjusted by creating small areas within the radiation field using multi-leaf collimators (MLC), and high-intensity radiation is delivered to the tumor. This helps in the death of cancerous cells while delivering low or minimal radiation to the surrounding critical organs for their protection.
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)
In VMAT treatment technique, the linear accelerator irradiates while rotating around the patient. During irradiation, small radiation fields are created by moving multi-leaf collimators, and intensity adjustments are made to the radiation beam. The dose rate changes throughout the irradiation time. Therefore, VMAT can be described as a dose-modulated technique with multiple arc angles. The treatment time varies depending on the treatment area but is generally shorter compared to other techniques.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS):
SRS is the process of delivering a relatively high dose of radiation to tumors and diseased lesions in the brain and central nervous system, while protecting surrounding healthy tissues, within one or several sessions. SRS requires millimeter accuracy and precision. Advanced imaging devices are used in SRS treatments to ensure precise tumor and patient positioning with image guidance. This allows very high doses of radiation to be delivered to the diseased area while protecting normal tissues. It is a non-invasive treatment model. The effects of stereotactic radiosurgery, typically performed in one or a few sessions, can be as sharp as surgical operations for some tumors.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is used for treating tumors that are well-defined and generally small in size. It is often used for brain tumors, brain metastases, spinal tumors, and spinal metastases. Supporting fixation tools are used to ensure the patient remains immobile during treatment.
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT):
In this treatment type, fewer sessions, smaller areas, and higher doses are used to treat tumors in any part of the body. In short, stereotactic radiosurgery applications outside the brain and spinal cord are referred to as stereotactic body radiotherapy. Tumors, due to their location, tend to move because of respiration or organ movement, making it difficult to keep them completely fixed. Determining tumor movement and considering it in high-dose stereotactic treatments helps deliver the desired dose accurately. For instance, a lung tumor's movement due to respiration must be tracked during treatment. Stereotactic body radiotherapy is used to treat small and isolated tumors, especially in the lungs, liver, adrenal glands, prostate, and pancreas.
```