Quick Connections

Eyyüp Kenan Özok
Since 2023, he/she has been working as an Internal Medicine specialist at Anadolu Health Center.
Speciality
- Internal Medicine
Education
University
- GATA Faculty of Medicine, 1988
Specialization
- GATA Haydarpaşa Training Hospital
Institutions Worked At
Graduation: GATA Faculty of Medicine 1988
Residency: GATA Haydarpaşa Training Hospital
Areas of Interest
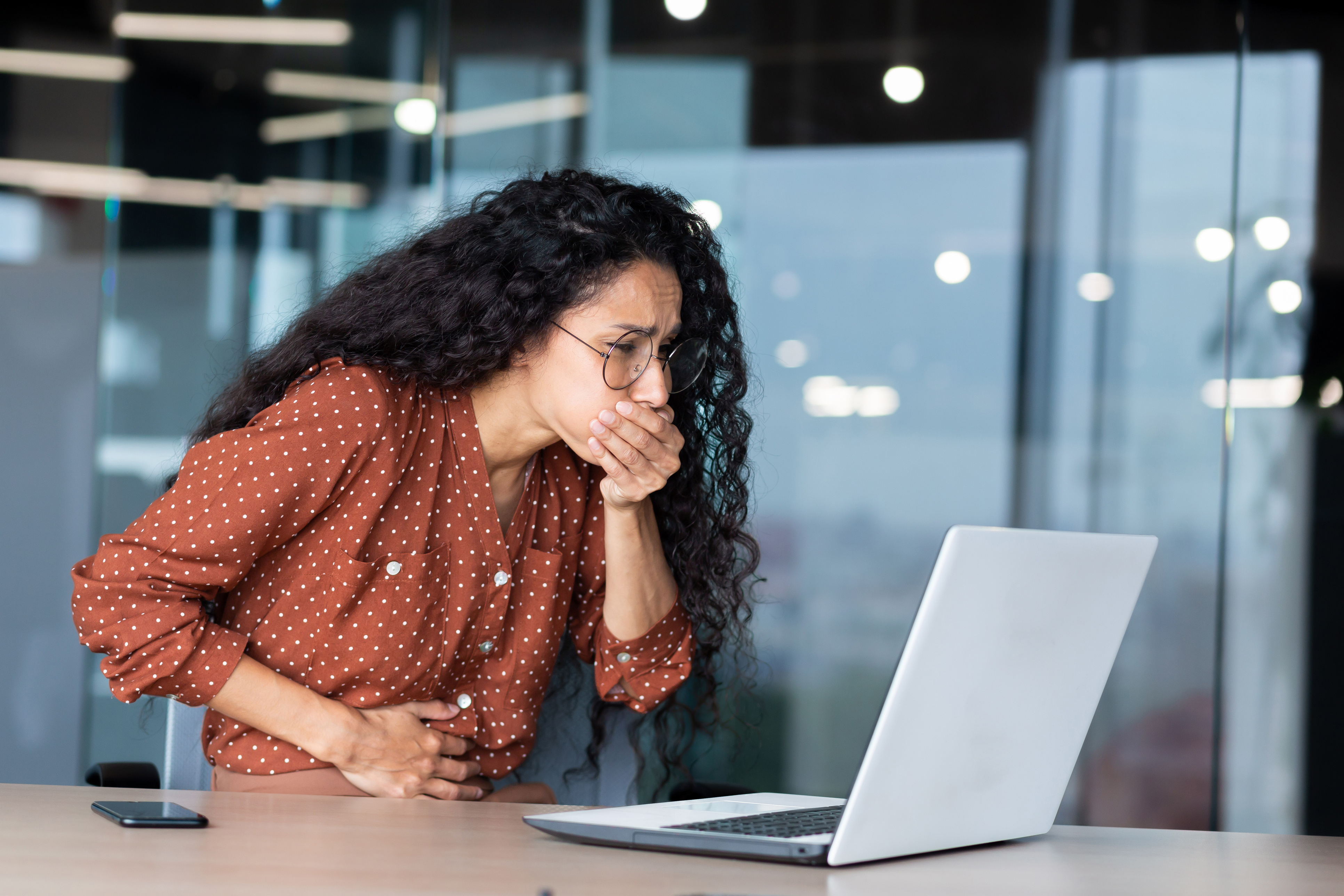

Vomiting is a digestive system disorder that results in the involuntary expulsion of stomach contents. It is usually preceded by a feeling of nausea and can be a symptom of many pathological conditions. Causes include infections, head injuries, cancer treatments, certain medications, poisoning, medical procedures, and illnesses. After vomiting, it's crucial to ensure adequate hydration due to excessive loss of water and electrolytes from the body. Some methods can be used to prevent vomiting when feeling nauseous, and after vomiting, certain practices can help compensate for the losses and damage in the body. To minimize the effects on the body, consuming tolerable amounts of water after vomiting is important. If vomiting is frequent and persistent, consulting a specialist healthcare provider is essential.
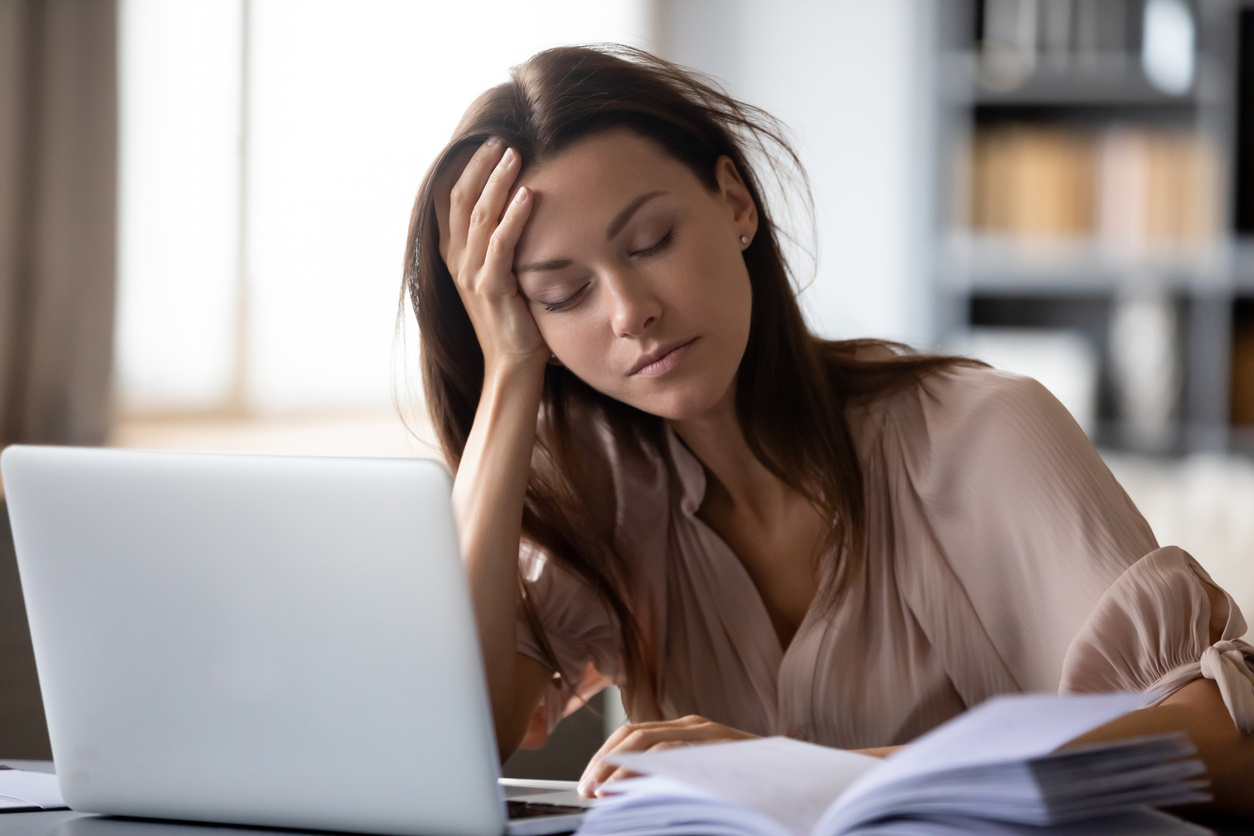

Anemia is a blood disease caused by insufficient levels of red blood cells in the blood. Anemia is also known as a deficiency in red blood cells and hemoglobin and can result from multiple factors. When anemia develops, a person may experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and cold hands and feet. Anemia typically arises from nutritional deficiencies. Therefore, doctors often prescribe vitamin supplements and provide dietary recommendations. These dietary recommendations are based on consuming foods rich in iron, folate, vitamins B12 and C. If you think you are at risk of anemia, you should consult a doctor.
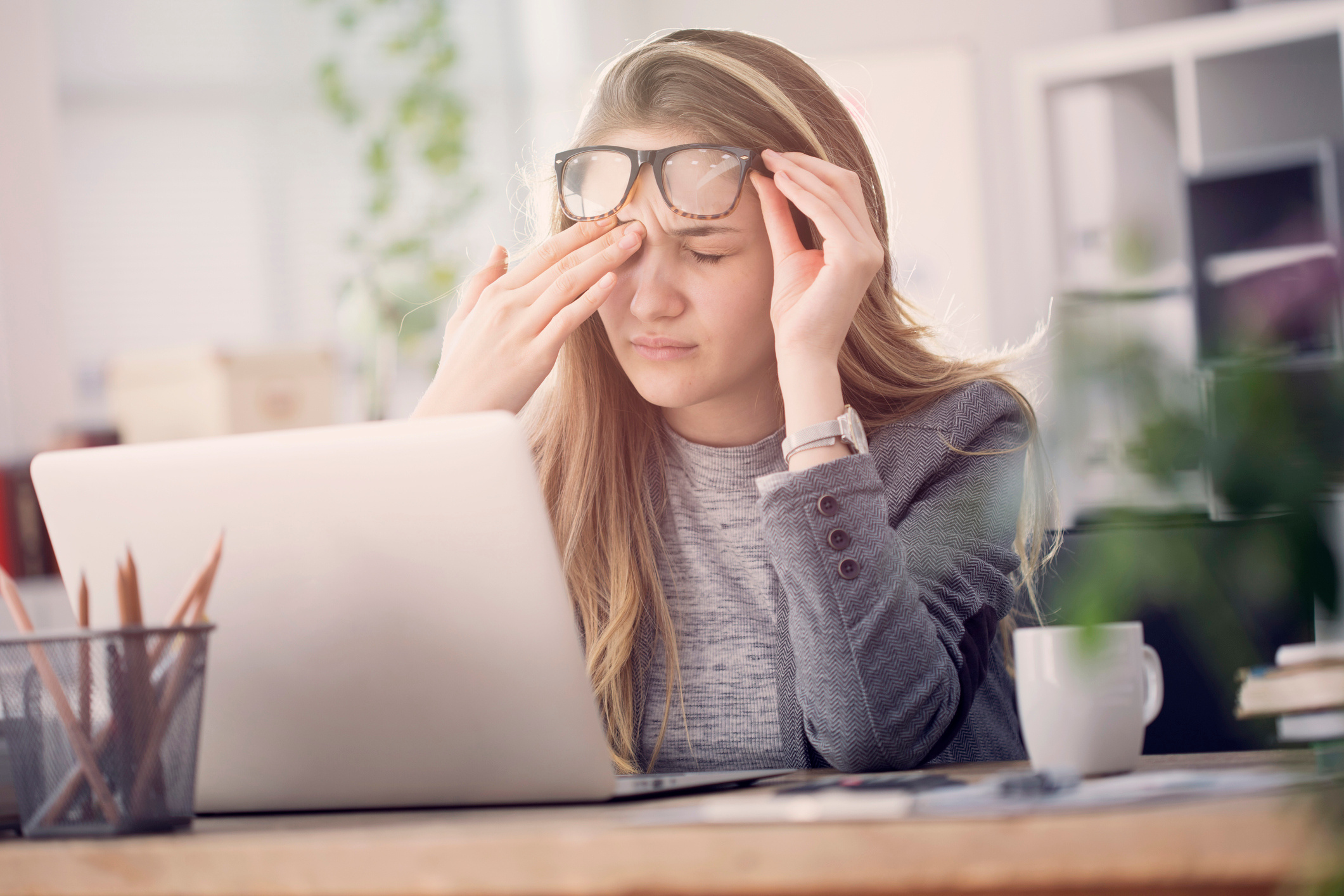

The complaint of fatigue can also be expressed as tiredness and exhaustion. All healthy individuals can experience fatigue when they engage in heavy tasks or do not eat adequately. This condition is usually temporary, and the person will regain their previous health over time. However, in some cases, these complaints can manifest as symptoms of chronic autoimmune diseases. Since prolonged fatigue may indicate a different illness, it should not be ignored, and seeing a doctor for examination can lead to an early diagnosis. Obesity and excess weight can restrict a person's movements, leading to fatigue over time. Additionally, individuals with below-normal weight may experience fatigue due to nutritional deficiencies. A proper diet that meets vitamin and mineral needs, along with an exercise routine suitable for the individual's age and health, can help alleviate fatigue problems. Paying attention to the consumption of grains, fresh fruits, protein sources, and healthy fats can contribute to feeling energetic. Changes in sleep patterns, restricting the intake of excessively fatty and sugary foods can help ensure a more energetic day. The amount of water consumed throughout the day should be maintained at levels that meet the body's needs, and if possible, mineral-enhanced waters should be preferred. Individuals experiencing issues such as stress and depression may face fatigue problems. Seeking psychological support for such issues can help alleviate their effects over time.
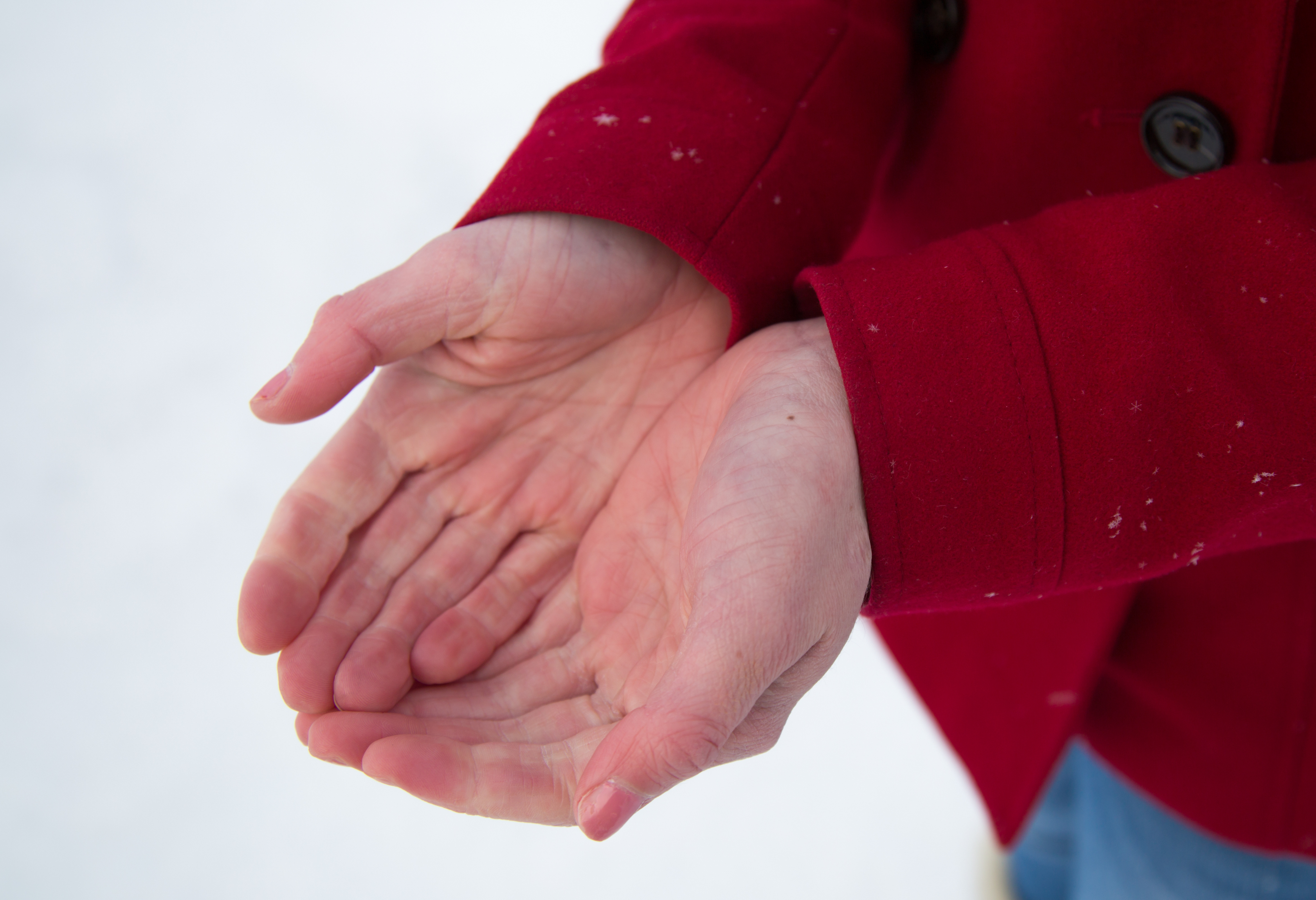

Raynaud's syndrome develops as a result of the contraction of blood vessels, leading to episodes in the extremities and is characterized by the interruption of blood flow. In Raynaud's syndrome, which generally requires the use of vasodilator medications for treatment, blood flow to structures such as the fingers or toes, ears, and nose can be disrupted. This condition, which occurs in episodes, is defined as vasospasm. Raynaud's syndrome is classified into two groups: primary (or idiopathic) and secondary. In primary Raynaud's syndrome, there is no underlying condition causing the episodes, whereas in the secondary form, attacks can occur due to conditions such as arthritis, frostbite, or various autoimmune diseases. You can follow the continuation of the text for more information about other topics related to Raynaud's syndrome.
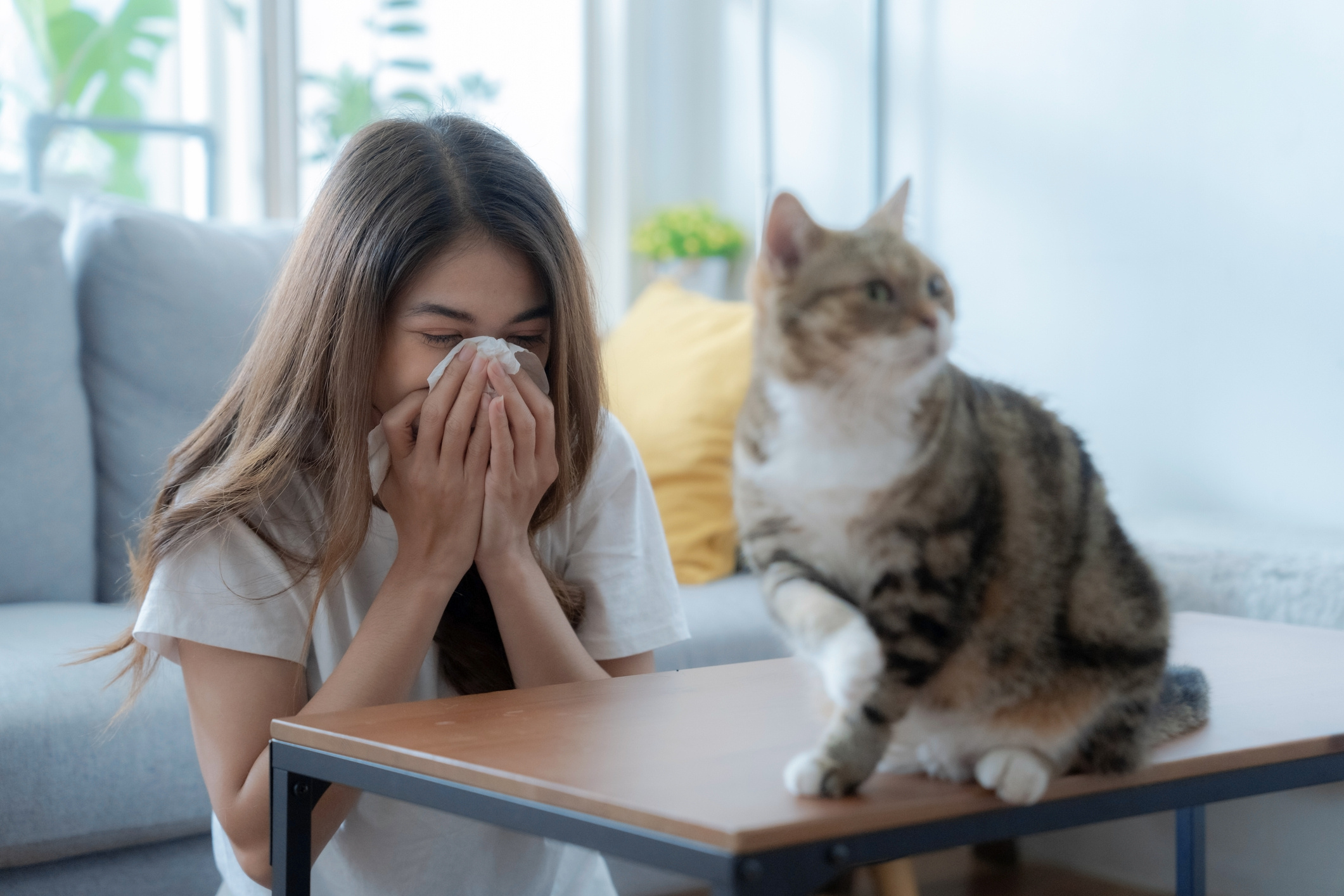

Cat allergy is a hypersensitivity to a cat's saliva, fur, skin dander, or urine. These substances, which trigger allergic reactions, are known as allergens. Cat allergy can range from mild respiratory symptoms, such as sneezing and runny nose, to severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. If you suspect a cat allergy, it’s essential to consult a doctor for symptom management and an appropriate treatment plan.
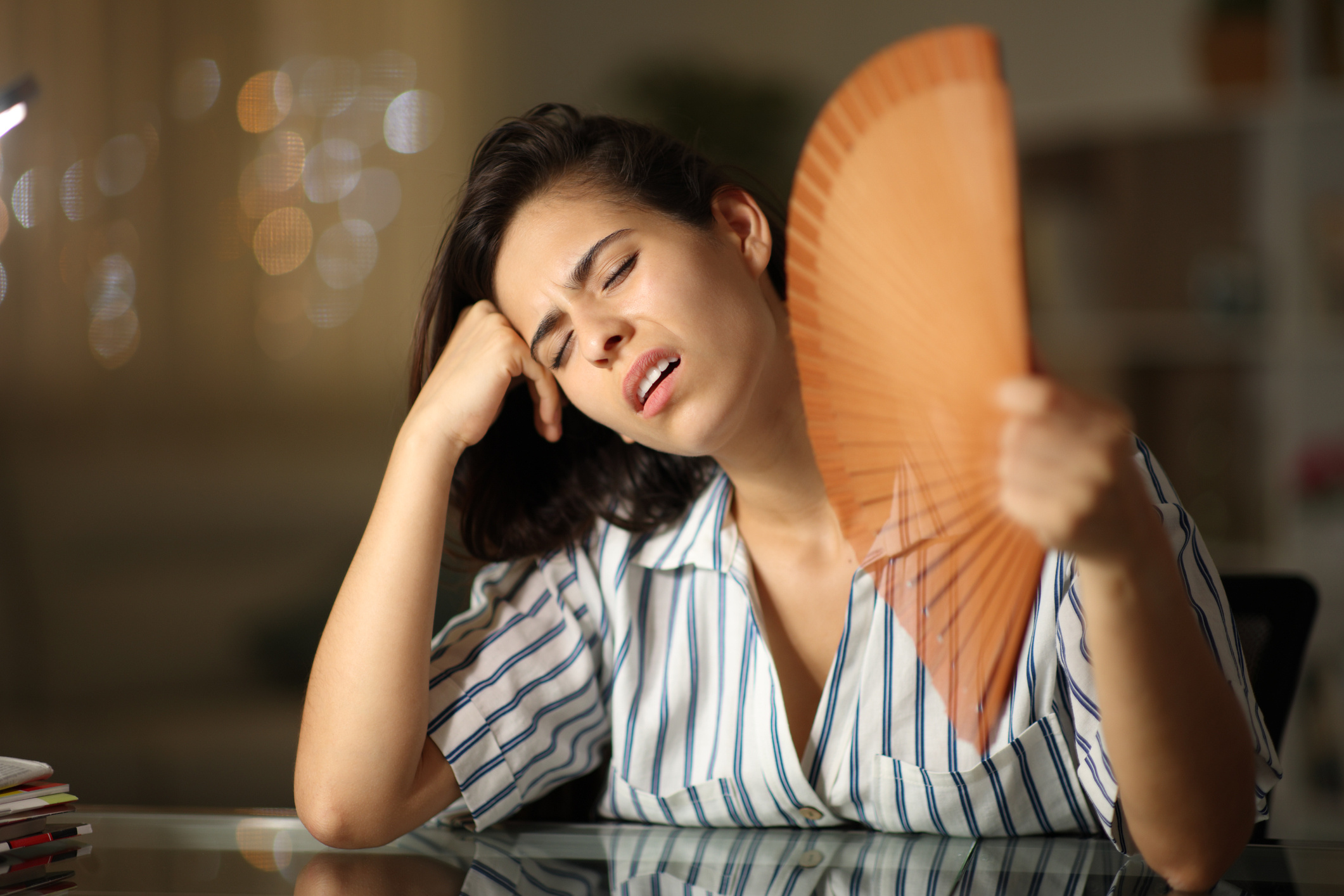

Individuals experiencing night sweats may find that their sheets or pajamas are soaked with water upon waking. Regulating the sleeping environment through various methods is the first step that can be taken to address this issue. In cases where night sweats occur due to an underlying medical condition, it is essential to consult healthcare providers for the identification of the underlying disorder and to consider appropriate treatment options. This condition, referred to as sleep hyperhidrosis, usually arises from manageable diseases, but it can also occur as a sign of life-threatening conditions, making it beneficial to be informed. You can follow the continuation of this article for more information on other topics related to night sweats.

As people age, the frequency of muscle wasting increases, with Prof. Dr. Çağatay Öktenli, an Internal Medicine Specialist at Anadolu Health Center, noting that 4 out of every 10 people over the age of 80 face this issue.
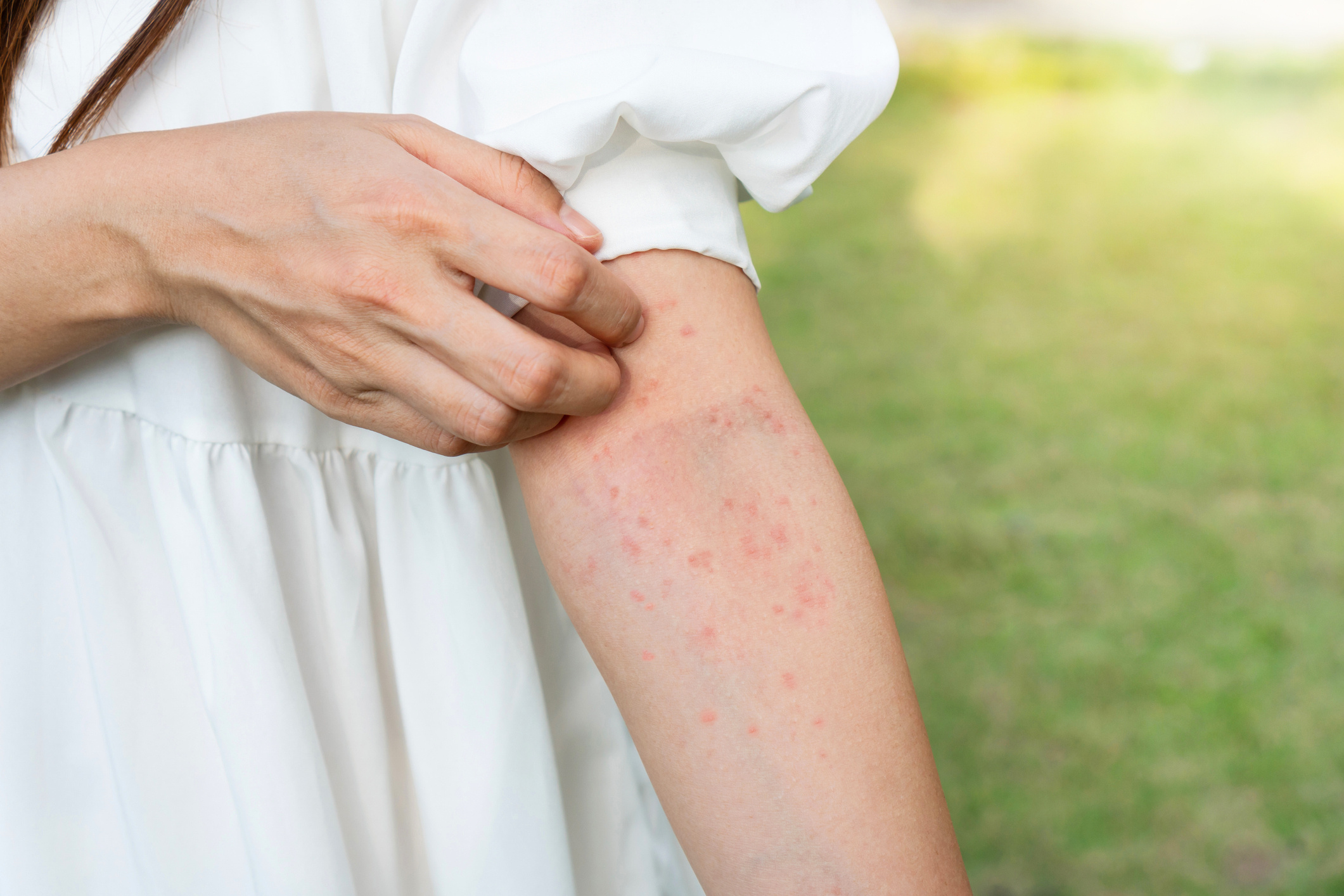

Mosquitoes are delicate creatures with small, short lifespans, long legs, and distinctive wings, easily recognizable. Typically appearing during summer nights, they are known for the itchy bumps they leave after biting. These noticeable itchy bumps are allergic reactions caused by a chemical mosquitoes use when they extract blood. The mosquitoes that feed on blood are usually females, as they require the proteins found in human or animal blood for reproduction. Male mosquitoes, on the other hand, feed on flower nectar and plant juices. A mosquito bite usually subsides within 24 hours and doesn’t cause serious problems, but it should be monitored for allergic reactions. In endemic regions, mosquitoes can transmit serious diseases like malaria, West Nile virus, dengue, filariasis, yellow fever, and Zika virus.
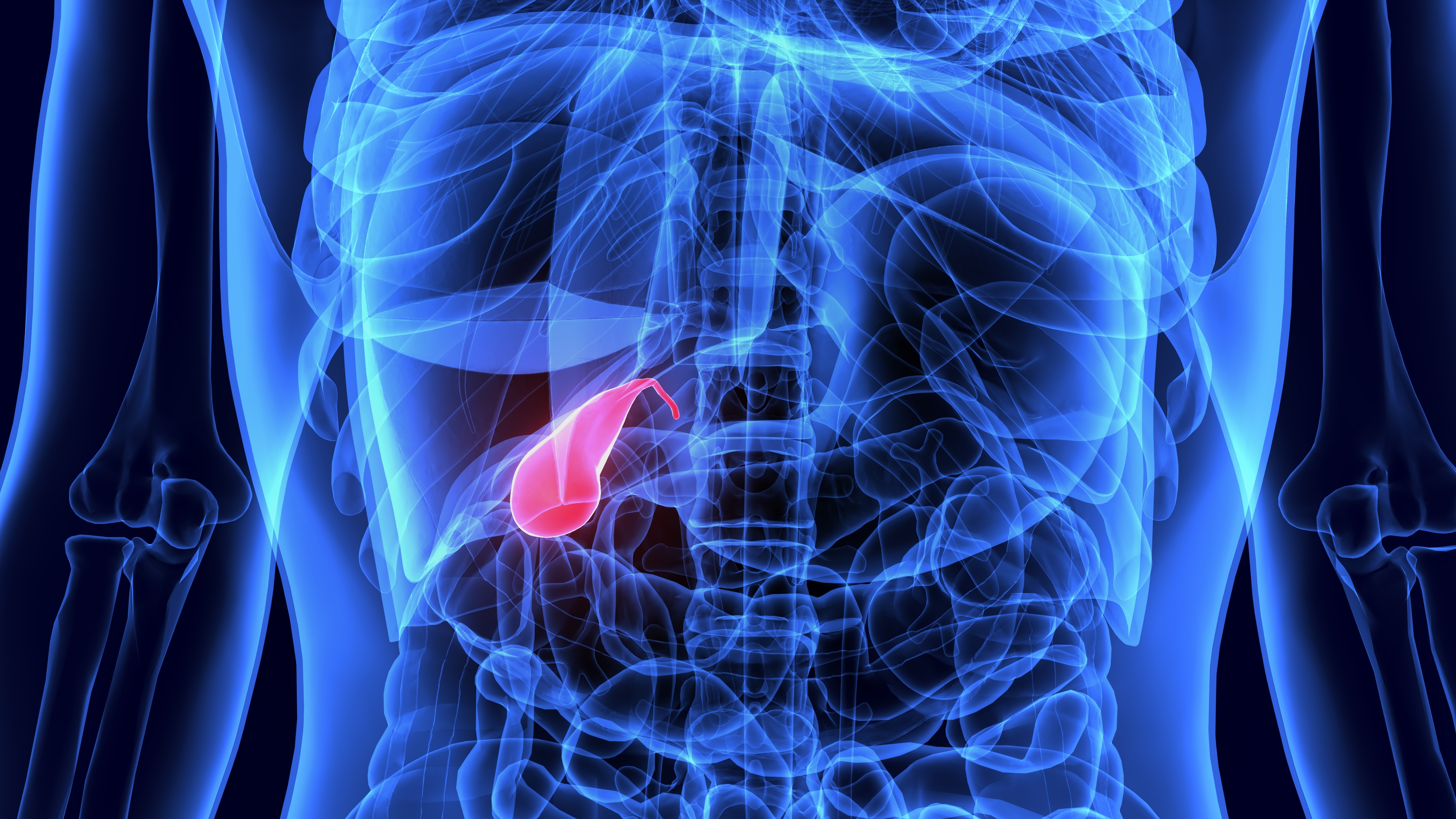
The human digestive system consists of two main parts: the organs within the digestive tract and the accessory digestive organs. The digestive tract—comprising the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus—plays a major role in digestion. For effective mechanical and chemical digestion of food, absorption of nutrients in the small intestine, calorie supply for cells, and elimination of waste through defecation, both the organs of the digestive tract and accessory structures such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder must work together in harmony.

Stomach pain is a common condition experienced by both children and adults. There can be numerous different causes of stomach pain. What causes stomach pain? What helps relieve it? You can find the answers to all these questions in the following text.

Creatinine is a compound found in the bloodstream of every individual, released as a result of metabolic processes. Creatinine is excreted from the body through the urinary tract and should be present in specific levels within the body. The amount of creatinine that should be present in a person's bloodstream varies according to age, gender, race, and body measurements. However, having creatinine levels outside of these parameters can be indicative of certain diseases. In particular, creatinine levels can be evaluated to determine whether kidney functions are operating healthily.
Cortisol is a hormone-like substance naturally synthesized in the human body. There may be diseases associated with its deficiency. Some patients may not synthesize sufficient amounts of cortisol in their bodies. Complete lack of cortisol synthesis is not possible in a healthy body. For these patients, cortisol replacement therapy, which has offered very effective solutions in recent years, is applied. This is because the effects of cortisol are undeniably important for the immune system and the body's ability to heal itself. In cases where it is not produced, exogenous synthetic hormones, meaning cortisol obtained from external sources, should be administered. The synthetic form of cortisol that cannot be synthesized in the body is called cortisone. There may be misconceptions in the public about the use of cortisol and cortisone, leading to the belief that cortisol has more negative effects. Of course, while cortisol treatment has negative effects, it also provides significant treatment opportunities for the patient. Every medication can have side effects, even if they are minor. The effects of cortisol treatment can be managed as long as doctor visits are not neglected and post-treatment recommendations are followed. Cortisol is a hormone produced in the outer part of the adrenal gland called the cortex. One of the naturally occurring hormones formed as a result of a series of biochemical reactions using cholesterol as a raw material is cortisol. Two different groups of hormones are produced by the adrenal gland: glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. In the glucocorticoid group, there are hormone-like products known as cortisol and cortisone. Both glucocorticoids, cortisol and cortisone, affect the body’s protein and carbohydrate mechanisms. Cortisone is actually the inactive form of cortisol. After its production, cortisone is processed in the liver to obtain the active form, cortisol. Therefore, the active form of cortisol is administered for the treatment of many diseases.

Calcium is an essential mineral with important functions that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet. Calcium is directly related to growth, development, the nervous system, the circulatory system, and bone health. Therefore, calcium deficiency can lead to some serious symptoms.

The diaphragm is the muscle that separates the chest from the abdominal cavity and plays a crucial role in breathing. A spasm of this muscle causes the vocal cords to close temporarily, resulting in the "hic" sound. Hiccups are uncontrolled, repetitive spasms or sudden movements of the diaphragm. Eating too much, drinking alcoholic or carbonated beverages, or sudden excitement can lead to hiccups. For most people, hiccups typically last only a few minutes and resolve on their own.
The Hepatitis C Vaccine is designed to combat Hepatitis C, a type of liver disease caused by the HCV virus. The Hepatitis C virus can cause chronic infection in the liver, potentially leading to permanent and life-threatening effects on the body. Millions of people around the world are infected with Hepatitis C, with nearly 1 million individuals in our country alone. Although this disease is currently treatable, it often becomes chronic due to late diagnosis in many cases. If diagnosed early without leading to other complications, complete recovery can be achieved.
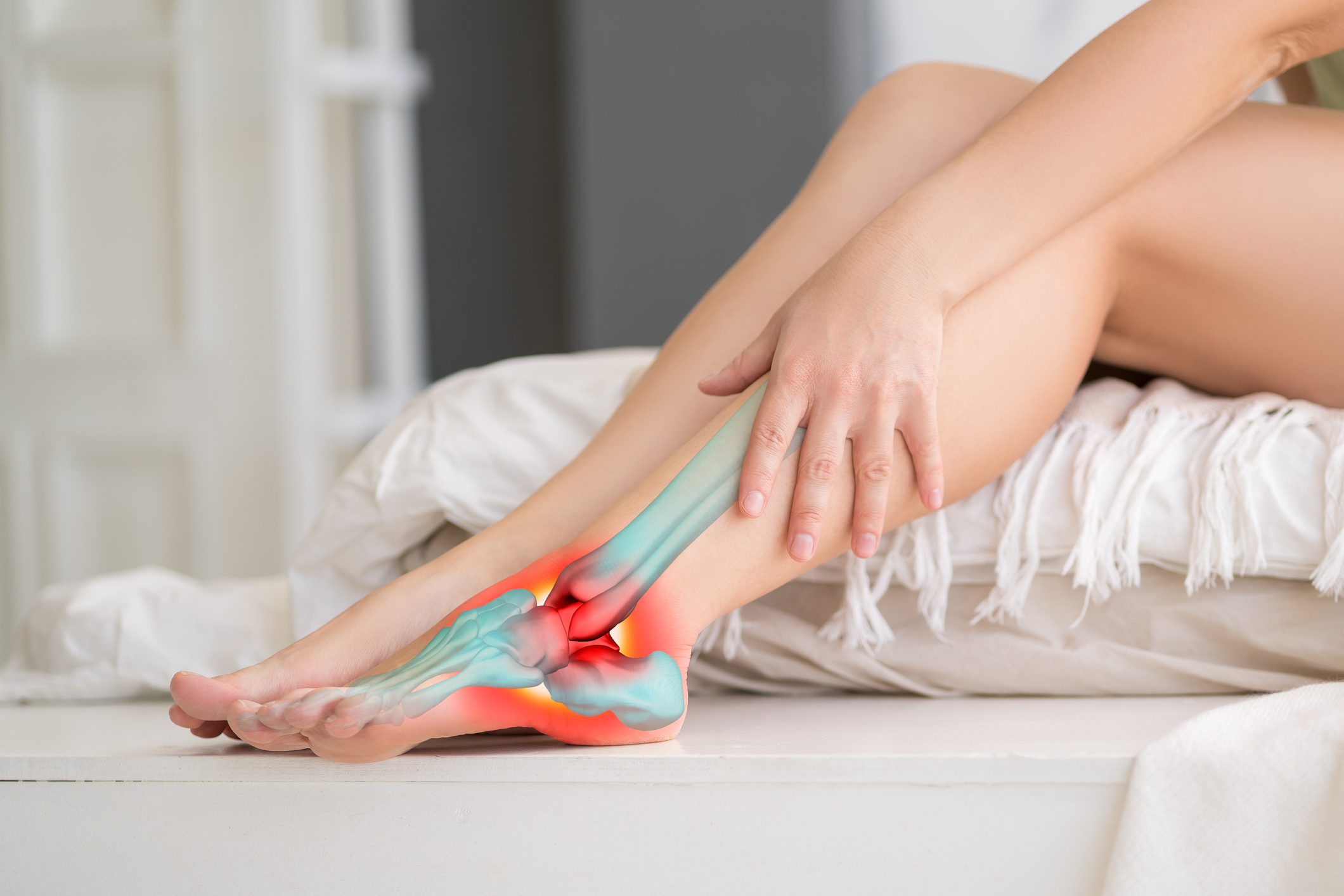

Historically known as the disease of kings, gout disease is characterized by an increase in uric acid circulating in the blood, leading to arthritis, or joint disease. The symptoms of gout develop based on the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints and the body’s reaction to them. Gout attacks typically occur at night without any prior warning. Many gout patients recover by paying attention to their diet and lifestyle, while some require medical treatment.
With glutathione therapy, the antioxidant capacity of our body is increased, making us more resistant to diseases.

Food poisoning can be briefly defined as conditions that are transmitted through food and primarily negatively affect the stomach and intestinal systems. Chemical substances, natural food toxins, metals, pesticides, plastics, detergents, parasites, bacteria, mold, and microorganisms like yeast can all be factors that cause food poisoning. Although the symptoms of food poisoning can vary from person to person, stomach discomfort, diarrhea, and vomiting are often common symptoms. To prevent food poisoning, attention should be paid to hygiene conditions. Discarding moldy foods, thoroughly cleaning kitchen utensils, and washing fruits and vegetables before consumption can be considered preventive measures. Appropriate treatments can be applied to affected individuals based on the severity of the symptoms and the factors causing the poisoning. Treatments can include fluid replacement, probiotics, antibiotics, and antiparasitic medications.

The healthy concentration of microorganisms in the gut, known as the microbiota, is an extremely valuable structure that directly or indirectly affects the functioning of all body systems, especially the digestive system. The microbiota, which is sterile until birth, begins to develop with birth and is largely influenced by the method of birth, dietary habits, and environmental factors. This microorganism concentration has a very delicate balance, which can be disrupted by unnecessary antibiotic use or unhealthy eating habits such as fast food, leading to an increase in harmful microorganisms, particularly on the intestinal surface. This disrupts the healthy structure of the gut and can lead to various diseases, including leaky gut syndrome.
The liver is the largest organ in the body and is considered the metabolic factory of the body. It is located in the upper right part of the abdominal cavity, beneath the diaphragm, and is responsible for the synthesis of many substances. Chronic liver diseases are one of today's significant health issues. In the advanced stages of chronic liver diseases, liver cells become damaged and swollen (ballooned). As the disease progresses, scar tissue forms in the liver, which is defined as fibrosis.

During the summer months, when temperatures and humidity levels rise, the need for fluids is higher compared to other seasons. The body breathes faster, sweats, and expels excess heat through urine to maintain its temperature against the heat. Approximately 65% of the human body is made up of water. An adult loses an average of 2.5 liters of fluid daily. In addition to fluid loss, minerals such as sodium, calcium, and potassium that regulate the body’s electrolyte balance are also expelled. Under normal conditions, the body can compensate for lost fluids and electrolytes through food and water intake. Reductions in the total fluid amount in the body manifest as feelings of thirst. If fluid loss increases, serious health problems can occur.

Vitamin D deficiency is a significantly common condition in our country. To prevent issues related to vitamin D deficiency, society needs to be aware of its importance. Eating a healthy diet and getting enough sunlight are crucial in preventing vitamin D deficiency.

Celiac disease is an immune system disorder characterized by chronic damage to various tissues on the intestinal surface, caused by both environmental and genetic factors. For genetically susceptible individuals, consuming certain grains like barley, wheat, and rye triggers a reaction in the body, and the protein called gluten found in these grains is perceived as a completely toxic substance by the immune system. Initially considered a gastrointestinal disease, this condition has been extensively studied in recent years, revealing that it significantly affects many systems, including neurological, psychological, hormonal, rheumatological, and cardiological systems. Lack of information regarding celiac disease can delay its diagnosis, which can particularly lead to growth and developmental delays during childhood. Therefore, having accurate knowledge about celiac disease and gluten intolerance is extremely important to support a healthy developmental process.
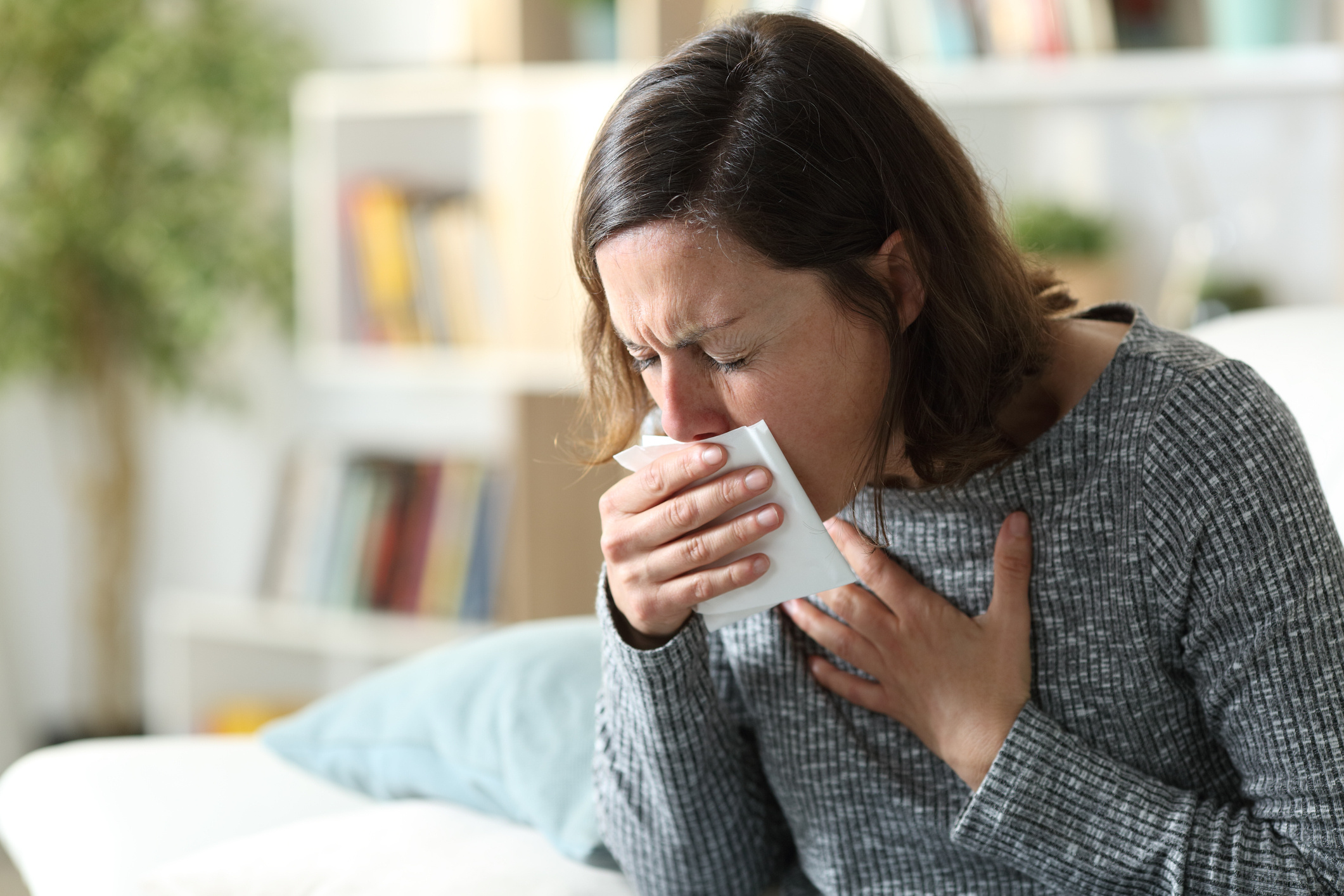

Sputum is a mucus layer that serves a protective lining. The mucus layer found in the respiratory tract prevents the area from drying out and becoming irritated. It acts as a protective structure against foreign substances such as dust and pollen that enter the body. The mucus layer changes in color and structure for various reasons, forming sputum. Generally benign, sputum can sometimes indicate a different health issue. In cases of respiratory and lung diseases, sputum production may increase due to irritation and infection. Therefore, sputum can provide preliminary information about health status. Additionally, home conditions, work environments, and habits can directly or indirectly influence sputum formation. Although producing sputum is seen as the body's way of cleansing itself, it is beneficial to monitor it closely. If there are changes in color, structure, or habit, the underlying cause should be investigated.
The immune system protects the body from foreign and harmful substances that enter through the nose, intestines, respiratory system, and skin. In some cases, the immune system's reactions to these foreign and harmful substances may be excessive. This condition is defined as an allergy. Although the exact causes of allergies, which may have a genetic predisposition, are not fully understood, certain allergens play a significant role in the development of the disease. Allergens are grouped into five main categories: environmental allergens (house dust mites, mold spores, pollens, animal allergens), insect allergens, food allergens, drug allergens, and occupational allergens.

Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetic disease primarily seen in Mediterranean countries. It is commonly found among Jews of Eastern European descent, Sephardic Jews, Spaniards, Greeks, Armenians, Arabs, and Turks. Although there is an ethnic predisposition, this disease can also affect other populations. The severity of lifelong FMF varies from person to person. Despite being known as Mediterranean Fever, it is more prevalent in the Central Anatolia region in our country.
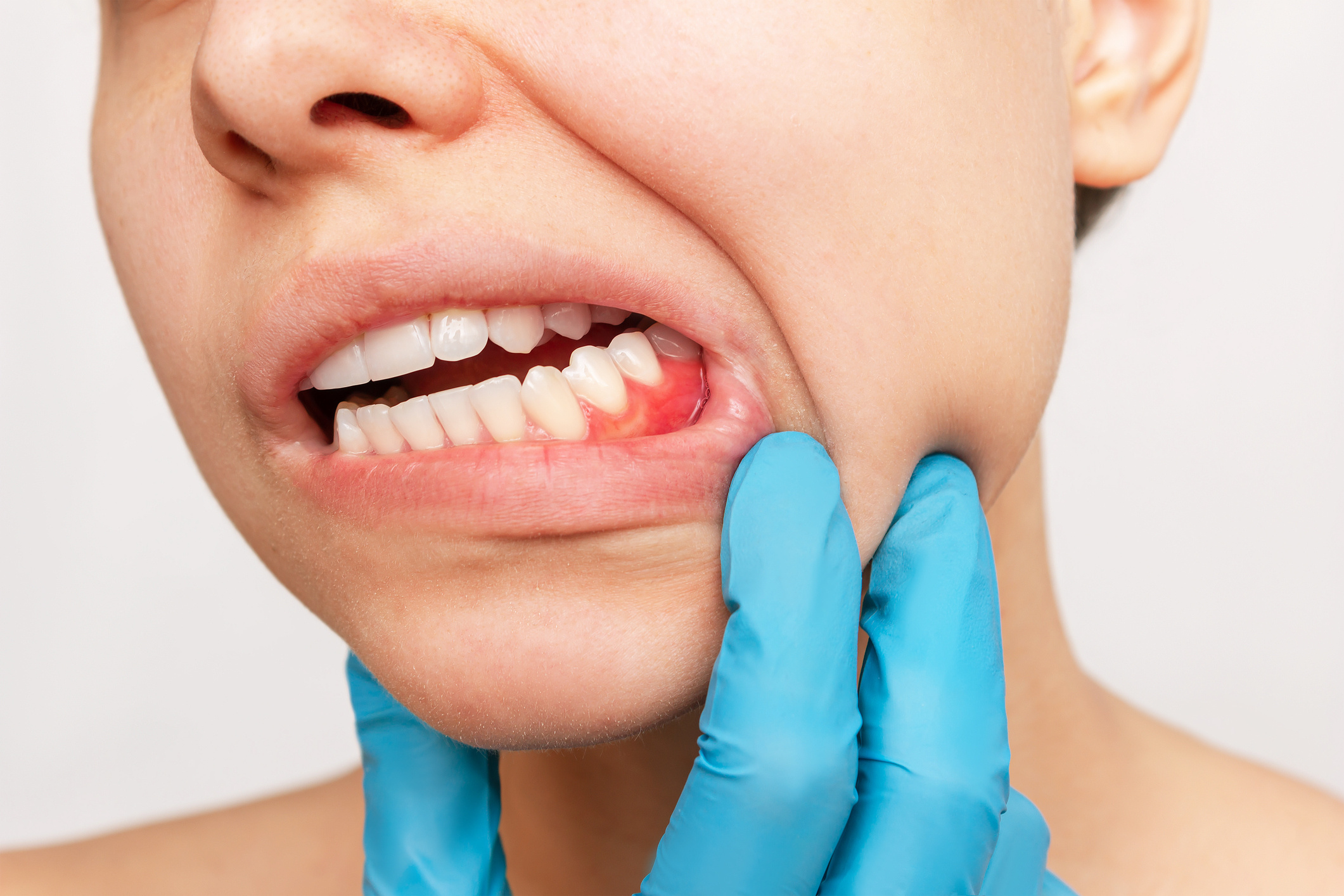
Aphthous ulcers, also known as canker sores, are small, shallow lesions that appear on the soft tissues inside the mouth or at the base of the gums. These sores can sometimes cause intense pain and difficulty with eating and speaking. Unlike cold sores, aphthous ulcers do not appear on the lips and are not contagious. Most aphthous ulcers heal on their own within one or two weeks. However, ulcers that continue to grow without healing may pose health risks, and it is essential to have these evaluated by a doctor.

In today's world, blood tests are the first assessment method for detecting most diseases. A complete blood count (CBC), or hemogram test, is performed on a large number of patients daily in hospitals, providing important information for both diagnosis and monitoring. The interpretation of blood tests by specialists, along with the patient's medical history and consideration of other diseases, guides the treatment the doctor will administer. The hemogram test compares the normal range of cell groups in the blood to the patient's cell count. Diseases can be diagnosed by identifying abnormal cells or an increased number of these cells in certain pathological conditions. By analyzing a few milliliters of blood from the patient, a laboratory can provide valuable information that guides treatment decisions

Hypothermia is characterized by a drop in body temperature below 35°C and is a condition that requires emergency medical intervention. The severity of hypothermia can vary. As the severity increases, the risk of death and coma also rises, while the body develops responses to protect itself in the early stages. Therefore, proper first aid methods should be applied until medical intervention can be provided. During the first aid phase, the person should be moved away from cold, windy, and wet conditions to a warm and dry area. In the first aid and medical intervention processes for hypothermia, there are two important goals: to prevent further heat loss in the patient and to increase body temperature.
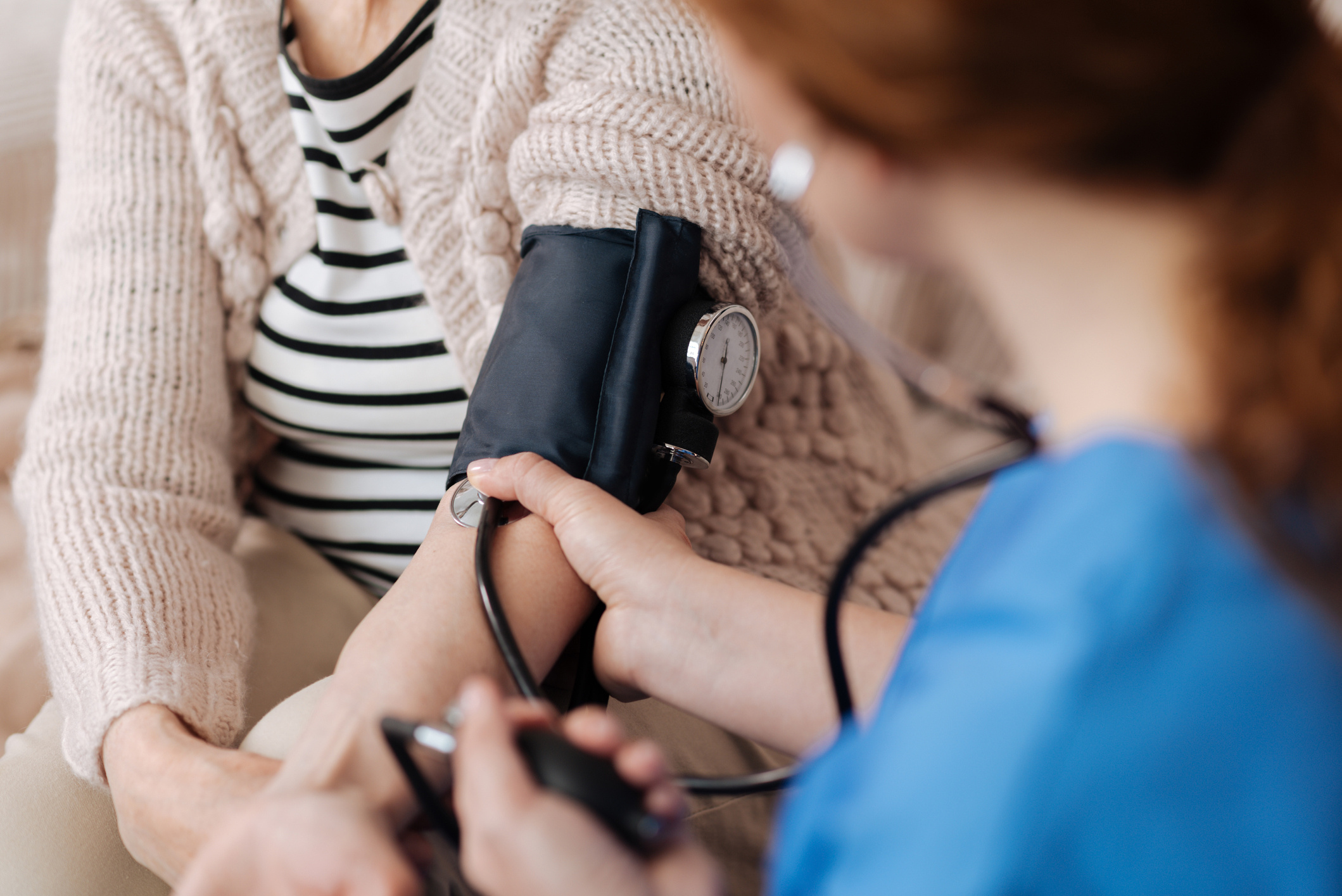

Blood pressure is an indicator that measures the resistance created by the blood pumped by the heart in the blood vessels. There are two different values for this pressure: systolic and diastolic. Systolic pressure, also known as high blood pressure, measures the blood pressure during the heart's contraction. Diastolic pressure, known as low blood pressure, refers to the measurement of blood pressure during the heart's resting phase. Low blood pressure is a health issue characterized by blood pressure being lower than the normal range. For healthy individuals, the ideal blood pressure is expressed as 120/80. Here, the value of 120 indicates systolic pressure, while the value of 80 refers to diastolic blood pressure. Low blood pressure is characterized by blood pressure values lower than 90/60. In some cases, low blood pressure may indicate a serious health problem. Especially in older individuals, low blood pressure can obstruct sufficient blood flow to the heart, brain, and other vital organs. This can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, and shock. Causes of low blood pressure may include dehydration, pregnancy, heart disorders, nervous system diseases, and certain medications. To prevent and treat low blood pressure, lifestyle changes such as drinking adequate amounts of water, increasing salt intake, rising slowly from a seated position, avoiding caffeine, eating low-carbohydrate meals, exercising the leg muscles, and wearing compression stockings can be applied. In some cases, medication treatment may also be recommended by a doctor.
Featured Cancer Articles
- 6 Nutrition Tips for Those Who Fast
- What is Disease X (Virus X)?
- How Does Cancer Form?
- What is an Ovarian Cyst?
- What is Cervical Cancer?
- What Are the Symptoms and Treatment Methods of Testicular Cancer?
- Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Process of Bladder Cancer
- Liver Cancer
- What is Stomach Cancer? What are Its Symptoms and Treatment?
- Thyroid: What is it, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment


